Cardiac Muscle Diagram, Anatomy and Clinical Significance
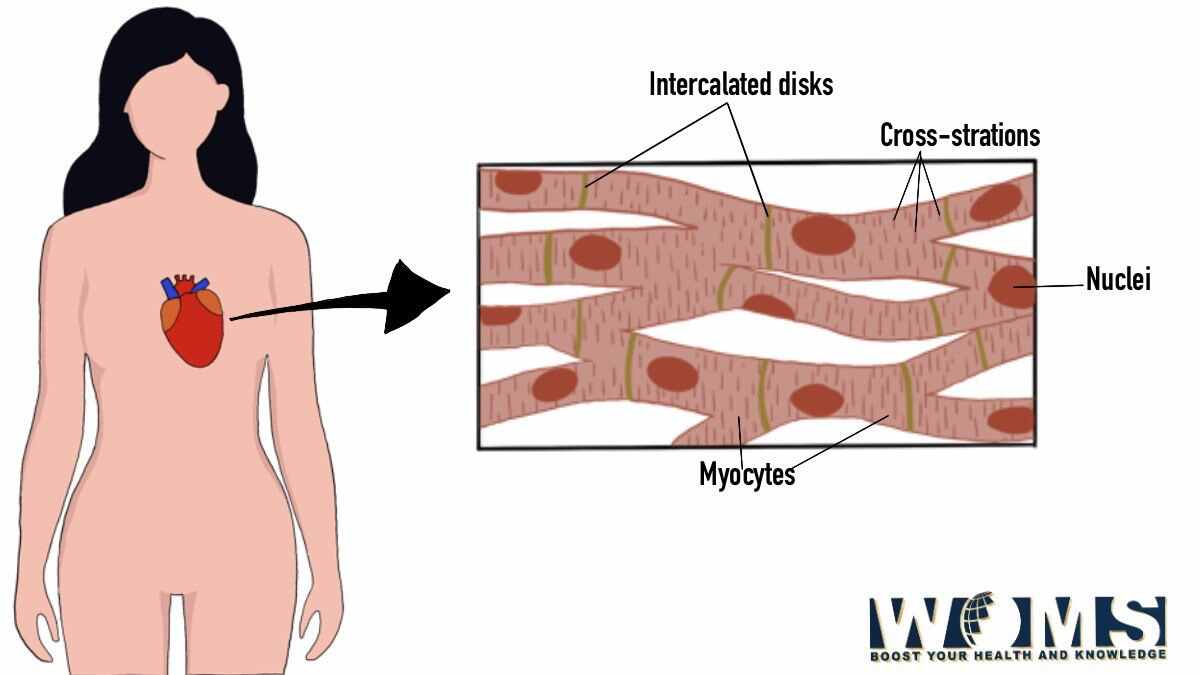
The cardiac muscle diagram is specifically associated with the muscles of the heart. These are involuntary but striated muscle tissue only present in the heart. In addition, cardiac muscles are also known as myocardium. The cardiac muscle performs the main function of balance contraction to pump blood throughout the circulatory system. Moreover, cardiac muscles are one of the main muscle types, quite similar to skeletal muscle.
Cardiac muscles are present between the outer (pericardium) and inner (endocardium) layers of the heart. This muscle forms a thick middle layer with abundant blood supply from the coronary blood circulation. A cardiac muscle diagram encodes different anatomical, histological, and several other aspects in detail to understand the basic concepts.
You should check this detailed article on overall diagram of muscle fiber in which we have mentioned all 3 muscle fibers in detail.
What are the main components of a cardiac muscle diagram?
Cardiac muscles are the main component of the heart to produce a wave of contraction to pump blood. Cardiac muscle contains several basic components to function in accordance. These are the basic units of a cardiac muscle diagram. These are as follows:
Intercalated discs
Intercalated discs are the small connecting units to join different units of cardiac muscle. These are the main units to transfer the wave of contraction along the whole thick layer of cardiac muscle. In this way, this layer acts as a basic functional unit to work synergistically.
Gap junctions
Gap junctions are also a part of cardiac muscle, working in combination with intercalated discs. When one muscle cell is activated, it transfers the stimulus toward the next cardiac muscle. In this way, these gap junctions are helpful to introduce a coordinate contraction.
Desmosomes
Desmosomes work the same as gap junctions. These are also present within the intercalated discs. In addition, desmosomes work to hold the cardiac muscle fibers together during contraction.
Nucleus
The nucleus is the main control center of the cardiac muscle. It is the main genetic material within the cell. Cardiac muscles have only one nucleus per cell. Do you know the answer to Do Red blood cells have nucleus? You should check the article to know it in details.
Gross anatomy of the cardiac muscle diagram
Cardiac muscle forms the bulk of the heart. These cardiac muscles form the middle layer of the heart known as the myocardium. Within the myocardium, there are several layers of cardiac muscle cells. When these layers contract, they squeeze the heart in various orientations. In this way, it expels the blood outside the heart with every heartbeat.
Histological details of the cardiac muscle diagram
According to the histological details of the cardiac muscle diagram, these are some of the microanatomical details.
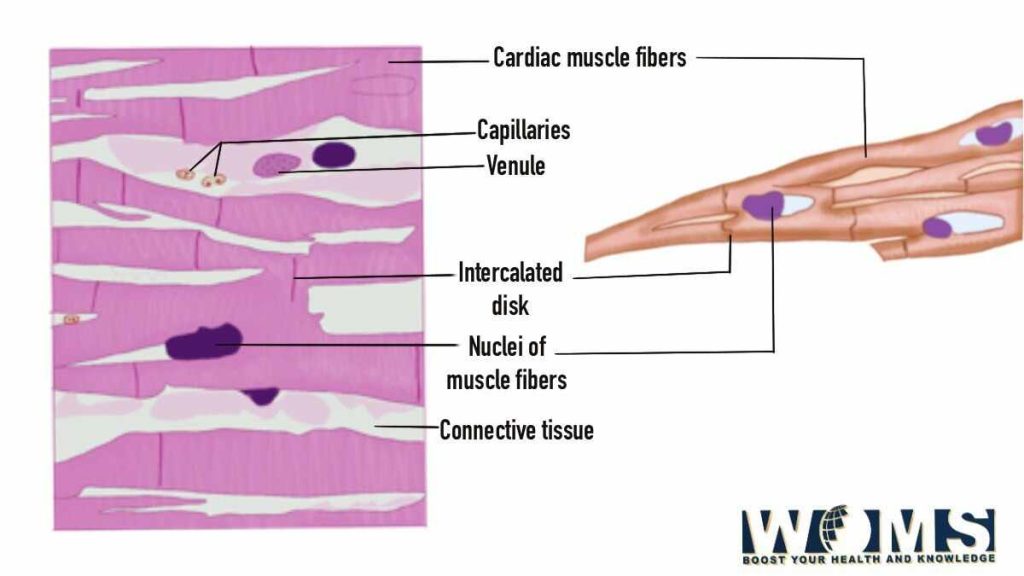
- Cardiac muscles are striated just like skeletal muscles with actin and myosin arranged within the sarcomeres.
- The cardiac muscle possesses a single nucleus.
- These cardiac muscles are branched with tight junctions in the form of intercalated discs.
- The cytoplasmic region contains smooth endoplasmic reticulum in the form of sarcoplasmic reticulum. It surrounds each myofibril.
Physiology of cardiac muscle diagram
Cardiac muscle is a well-organized muscular tissue with a close resemblance to skeletal muscle. It exhibits quite similar physiology and morphology. Cardiac muscle is made up of muscle fibers containing multiple thick and thin contractile filamentous units. These contractile units offer a peculiar striated shape to the cardiac muscle. Each cardiac muscle contracts and produces sufficient force. As a result, the size of heart chambers decreases with the simultaneous ejection of the blood into the circulatory system.
The main components involved during the excitation process are:
- Plasma membrane
- Transverse tubules
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum
- Mitochondria
How does cardiac muscle function for the heart?
The cardiac muscle provides the necessary force to pump the blood into the circulatory system. These muscles offer involuntary forces to force blood out of the heart. It is one of the main functions of the cardiac muscle that differentiates it from other muscle groups.
Cardiac muscles work through specific cell units known as pacemaker cells. These cells are proficient to maintain the coordinated contractions of the heart. Himan’s central nervous system transmits signals to these cells to maintain the balance between contractions. It maintains the heart contractions in a way that either slows or speeds up the heart contractions.
These contractile units, pacemaker cells, are coordinated with the cardiac muscle cells, making it easy to spread signals along the cardiac muscle. In this way, it produces a continuous wave of contraction to initiate a heartbeat.
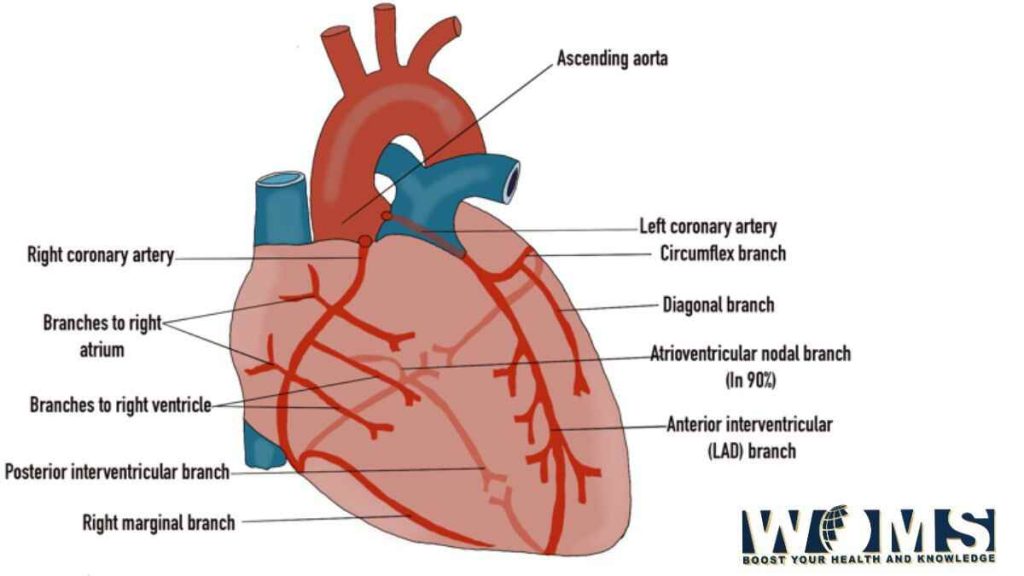
Blood supply of cardiac muscle
Cardiac muscle requires a continuous supply of oxygenated blood with enough nutrients to meet the energy demands of the body. Blood supply to these cardiac muscles is through the coronary artery, the first branch of the aorta. Whereas, the blood is drained into the cardiac veins to ultimately drain into the vena cava.
Lymphatic drainage of the cardiac muscles
Lymph drains into the myocardial plexus present within the myocardium. This myocardial plexus drains into the subepicardial plexus.
Innervation of the cardiac muscle:
The cardiac muscle is regulated by the autonomic nervous system with complete control over heart rate, cardiac output, contractility, and strike volume. Parasympathetic nerve supply is through the vagus nerve. Whereas sympathetic nerve supply is through the fibers of the sympathetic trunk exoting from the upper part of the thoracic spinal cord.
Clinical significance of cardiac muscle diagram
There are several diseases that can affect the health of cardiac muscle. These are some of the common clinical problems that have higher morbidity rates associated with mortality rates. Let us have a look at these diseases to highlight the clinical importance of cardiac muscle.
Ischemic heart disease
Ischemic heart disease indicates a pathological imbalance between the need and supply of oxygenated blood. It occurs when there is a decrease in the oxygenated blood supply to the cardiac muscle. This type of condition may occur during coronary artery atherosclerosis. Ischemia indicates a decreased perfusion of the cardiac muscles.
There are several other medical conditions that are associated with the ischemic syndrome. These are as follows:
- Acute myocardial infarction
- Cardiac death due to decreased blood supply
- Angina pectoris
Ischemic attack on the cardiac muscle may cause irreversible damage to the cardiac muscle, leading to the complete loss of function.
Cardiomyopathies
Primary diseases of the cardiac muscles are also known as cardiomyopathies. Damage to the cardiac muscle can also happen due to increased blood supply. These are associated with infectious agents. These infections may have bacterial or viral etiology.
Cardiac hypertrophy
Cardiac hypertrophy indicates an increase in the size of cardiac muscle tissues. To compensate for the larger size of these cells, the cardiac muscle cells require more sarcomeres and mitochondria to produce sufficient energy dose. Cardiac hypertrophy indicates a high metabolic rate with increased oxygen demands. But as a result, it provides a very low output due to increased consumption. In this way, this condition increases the workload with higher chances of ischemia resulting in cardiac failure and ultimately death.
Cardiac muscle injury
Any injury or trauma to cardiac muscle may damage the capability to function normally. Cardiac muscles have a very low regeneration potential to heal back. Such injuries can cause a complete loss of contractile myocardium pe may form scar tissue. These scars may decrease the contraction potential of the heart.
Surgical consideration of cardiac muscle diagram
There are also multiple clinical procedures that are associated with cardiac muscle diagrams. There are some surgical procedures that require proper clinical practice.
Cardiopulmonary Bypass
This surgical procedure is performed during cardiac surgery to discontinue cardiac contraction while maintaining the perfusion and oxygen supply to other organs of the body.
Conclusion
Cardiac muscle diagram indicates the complete anatomical details of cardiac muscle tissue. It dictates the functional unit of cardiac muscle to contract the heart and pump the blood in the circulatory system. The cardiac muscle is the main functional unit of the heart to provide sufficient force to pump blood outside the heart. These cardiac muscles work in a junction to produce a continuous wave of contraction to perform accordingly. Moreover, these contractions are coordinated to provide a continuous heartbeat without stopping.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
What kind of cells is present in a typical cardiac muscle?
Cardiac muscle is a well organized structure containing different types of cells to perform functions. These cells are of types and are as follows:
● Smooth muscle cell type
● Cardiomyocytes
● Fibroblasts
What is the characteristic feature of a cardiac muscle, differentiates it from other muscle types?
Cardiac muscle is specific by its nature and function. Considering the morphology of the cardiac muscle, it contains intercalated discs that connect each cardiac muscle unit. In this way, the whole layer of the myocardium works as a unit. This feature is quite distinctive.
Whereas, regarding physiology, cardiac muscle provides sufficient force to contract the heart. In this way, the heart ejects all the oxygenated blood into the circulatory system. This function is specific to the cardiac muscle.
Which thing controls cardiac muscle to function appropriately?
Unlike the other muscle types, cardiac muscle is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It controls either speeds up the heart contraction or slows down these contractions.