Anatomy and Overview of Anterior tibial artery
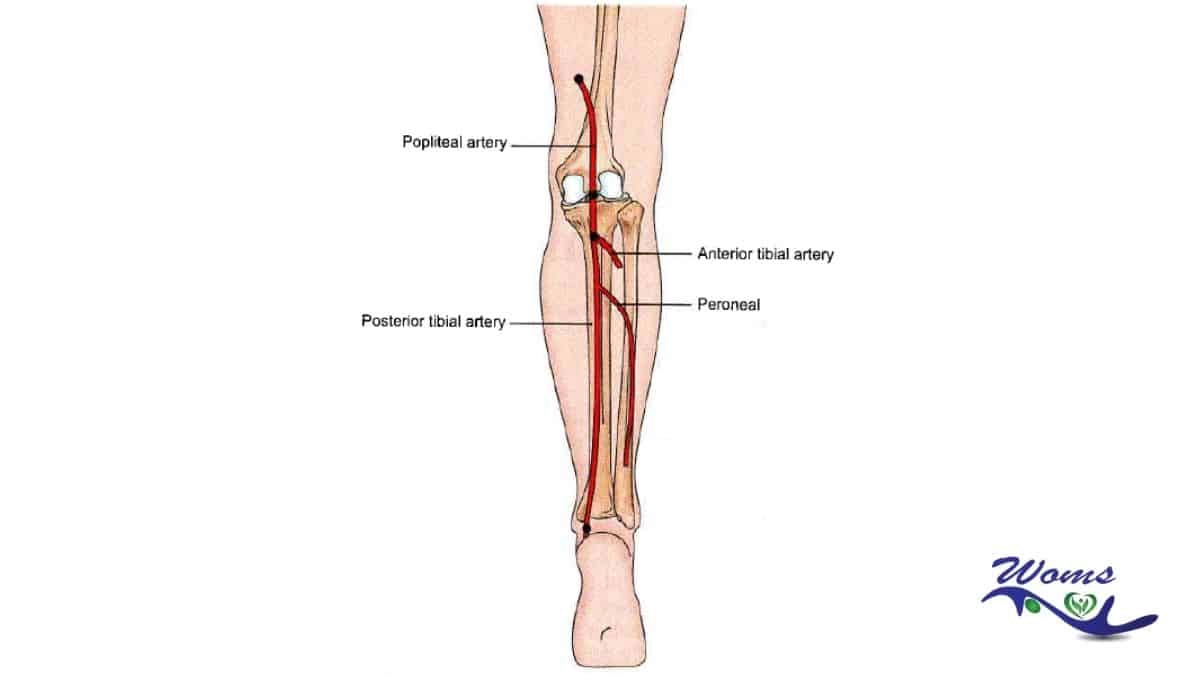
The artery called popliteal gives one of the terminal branches which is known as the anterior tibial artery. It lies in the leg’s posterior compartment and arises below the popliteal fossa. However, the majority of its course is located in the extensor part of the leg. The artery terminates at the level of the joint called the ankle joint, where it gives of its terminal branch, the dorsalis pedis artery. The artery’s pulse can be palpated near the origin of the artery called dorsalis pedis. An anterior tibial pulse can be felt in the middle of foot’s dorsum.
It is the principal artery that supplies blood to the Extensor part of the leg. It also supplies blood to the dorsal surface of the foot. The blood is supplied to the extensor part of the leg by the peroneal artery’s perforating branch, the size of which is conversely proportional to that of the artery.
Beginning, course and termination
The popliteal artery gives the smallest terminal branch which is the anterior tibial artery. At the popliteus’s border which is an inferior one that appears on the back of the leg opposite to the tibial tuberosity.
In the inter-osseous membrane’s upper part there is an opening through which the artery enters passing close to the fibula to the leg’s anterior compartment.
The artery runs downwards vertically to a point midway between the two malleoli in the anterior compartment of the leg, where it called the artery called dorsalis pedis .
Relations of anterior tibial artery
The artery lies between the two muscle called as tibialis anterior and the extensor digitorum longus in the upper one-third of the leg.
It lies between the tibialis anterior and extensor hallicis longus in the middle one-third.
In the lower one-third it lies between the muscle called as extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus muscle. In understanding these relations note that the artery is crossed from lateral to medial side by the tendon of the extensor hallucis longus.
The anterior tibial artery is associated by the venae commitantes. The nerve called deep is oblique to it in its above and down thirds, and beginning to it in its middle one-third.
Branches of the anterior tibial artery
- Its muscular branches supplies to the adjacent muscles.
- Anastomotic branches of the artery goes to the knee and ankle part of the body.
Round the knee joint the artery and posterior tibial recurrent branches anastomoses here. The anterior medial malleolar and anterior lateral malleolar branches take part in the anastomoses around the joint called ankle joint or malleolar networks.
The lateral malleolar network lies just below the lateral malleolus.
The medial malleolar arrangement lies just down the medial malleolus.
Anatomical variations
The anterior tibial artery can have several anatomical variations concerning its origin, caliber, course, and termination.
The artery may occasionally be of small caliber or rarely, absent. In this case, its supply is functionally replaced by the posterior tibial artery’s perforating branches or by the fibular artery’s perforating branch.
The anterior tibial artery may take on a different course, running along the leg’s lateral side, only to regain its anterior position at the level of the ankle joint.
The anterior tibial artery may occasionally terminate before reaching the foot’s dorsum. In this case, the dorsalis pedis artery arises from one of the fibular (peroneal) artery’s perforating branches.
The anterior tibial artery may occasionally be of large caliber, in which case it supplies both the foot’s dorsum and the plantar arch.
Main function
Supplying blood to the leg’s anterior parts muscles is its main function.
Clinical significance of anterior tibial artery
The anterior tibial artery is vulnerable to damages during a tibial osteotomy. It is because the anterior tibial artery passes the fibular neck medially.
How to palpate the anterior tibial artery?
In the foot’s middle dorsum, just edgeways of extensor hallucis longus muscle’s tendon anterior tibial artery are felt. It is also called an anterior tibial pulse. With the patient lying down to supine position, flex their knee to 45 degrees to the horizontal.
Takeaway:
It lies in the leg’s posterior compartment and arises below the popliteal fossa. However, the majority of its course is located in the extensor part of the leg. The artery terminates at the level of the joint called the ankle joint. At the same place where it gives of its terminal branch, the dorsalis pedis artery. The palpitation of the artery’s pulse is near the origin of the artery known as dorsalis pedis . The pulse that can be seen near this artery is called the anterior tibial pulse.