Anatomical Relationship of the superior sagittal sinus with sagittal midline
For surgical treatment of midline tumors as well as vascular diseases in & surrounding the 3rd ventricle, the interhemispheric strategy often comes into utilization. Throughout the neurosurgical technique, the superior sagittal sinus (SSS) is the one into disclosure.. And its full exposure significantly improves the operating angle vision of superficial structures.
The necessity for secure surgical entry sites as well as a tridimensional understanding of brain components. By using X-ray imaging has contributed to the hunt for textures and markings on the skull to conduct secure cranial operations.
The SSS comes into use in neurosurgical procedures to estimate the site of the superior sagittal sinus which is an external & marking of SSS between the bregma and the lambda.
Therefore, an exterior anatomical boundary is useless anterior to the bregma, as well as research, has shown that the position of the SSS is inaccurate.
More information of Superior Sagittal Sinus
Due to the danger of accidental damage to the sinus and bridging veins, that may induce numerous neurological abnormalities. The total exposure of the superior sagittal sinus to create a sufficient functioning area for the midline injury is challenging.
To assist neurosurgical planning, there should first understand the neuroanatomy of the SSS, and its connections with exterior surgical and landmark markers.
While there have been some investigations on the anatomy of the superior sagittal sinus as well as its connection with the sagittal suture. The majority of the investigation was on cadaveric samples with a small variety of cases, & more research is in need.
Our goal is to correctly characterize the location and deviation of the SSS to the sagittal midline.
Techniques that is in use to locate Superior Sagittal Sinus
The study by using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was obtained from our electronic health proceedings. Young patients who came to visit our hospital’s healthcare services between March-2018, as well as February-2020, had no abnormal imaging results were involved in the research.
Where is Superior Sagittal Sinus located?
The measurement of the length of the superior sagittal sinus at the following sagittal midline convexity craniometric abbreviations: (Na-Br) midway between the nasion as well as bregma, Br in the bregma, Br-Lamb middle between the bregma & lambda, & Lamb in the lambda.
Following that, we determine the dislocation of the superior sagittal sinus to the lateral sides, with relation to the sagittal midline in those surroundings. The predominant transverse sinus, which mainly empties the superior sagittal sinus, was seen too. [ Figure 2 ].
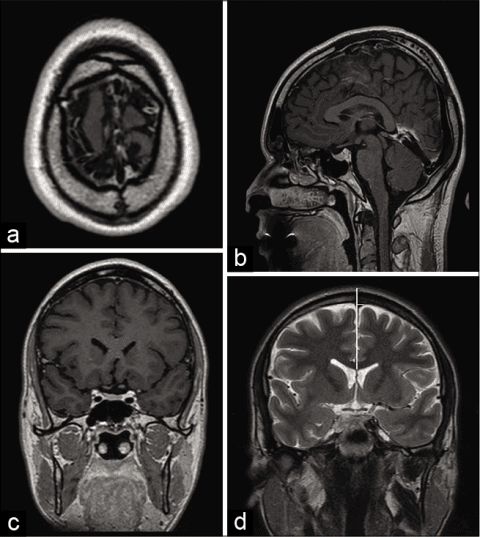
Figure 2: Position in the axial (a), sagittal (b), & coronal (c) planes of magnetic resonance imaging, & also measurements at the bregma in a coronal magnetic resonance picture in the T2 series (d). A vertical while lime marks the sagittal midline. The width between the sagittal midline and the superior sagittal sinus’s right and left edges. The superior sagittal sinus has shifted to the left at bregma, as seen in this picture. The bregma is the space at the top of the skull that is hypointense (d).
Anatomical key points:
Nasion: The place where the frontal & nasal bones meet is situated in a sunken region which links the nasal bridge with the glabella.
Bregma: The place where the frontal and sagittal sutures meet. To properly identify it in the sagittal plane, it was first identified in the top axial plane of the skull. It shows as a hypointense line that breaks the hyperintense bone signal’s full-thickness symmetry.
Lambda: The place where the lambdoid and sagittal sutures meet. To properly identify it in the sagittal plane, it was first identified in the top axial lines of the skull. It shows as a hypointense line that breaks the hyperintense bone signal’s full-thickness consistency.
MRI data acquisition as well as image processing
Coronal T2 MRI was attained utilizing a 1.5-T MR imaging part with a multi-slice examining attainment procedure. Intravenous contrast supervision was not necessary.
The image development as well as the evaluation was by the software Osiri-X MD image curriculum, version 11.0 in axial, coronal, as well as sagittal planes for the subsequent abbreviations: Na-Br, Br, Br-Lamb, as well as Lamb.
Why Superior Sagittal Sinus is analytically important?
Retroactive cross-sectional surveillance research was conducted. The Statistical Software Package was used for all results. The assumption of normality was tested using the Shapiro–Wilk test. We utilized the intraclass association coefficient for the interobserver reproducibility study.
For categorical variables, the number indicates was computed. The mean and standard variability of persistent information was also calculated. To evaluate means across groups, a two-tailed autonomous test t was used. Statistical importance was characterized as P 0.05.
The anatomical course of the superior sagittal suture
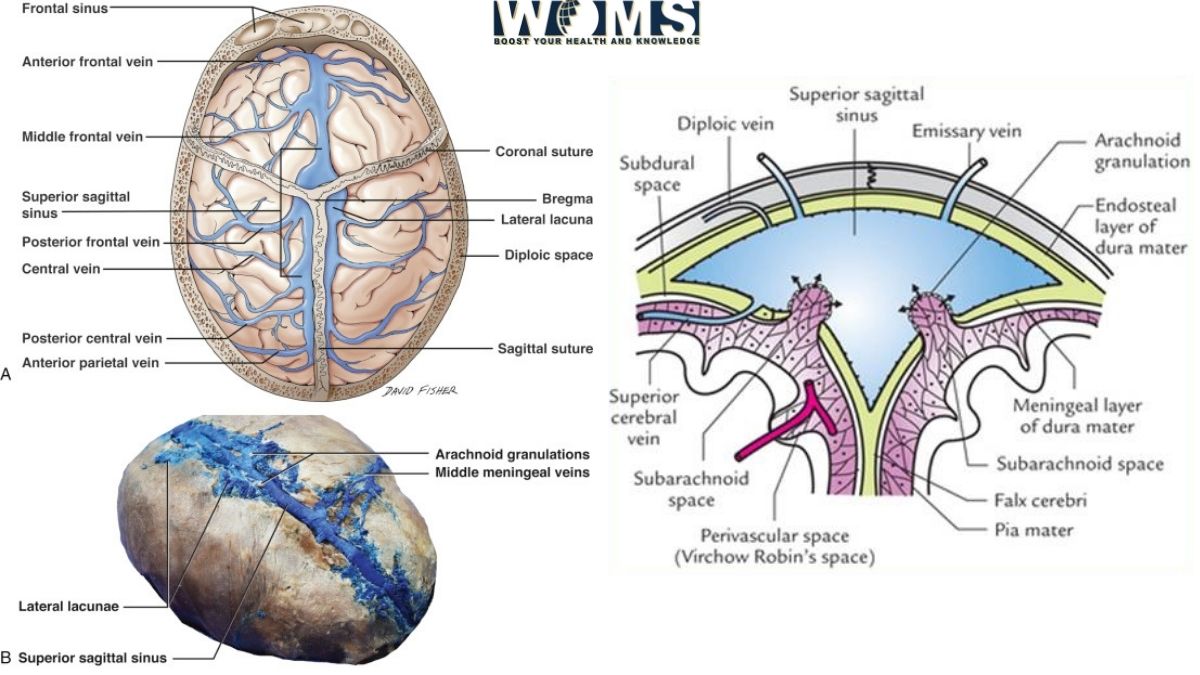
The SUPERIOR SAGITTAL SINUS is the highest dural sinus, running in the middle alongside the superior rim of the falx cerebri, starting from the back the frontal bone and growing superior as it moves posterior aspect. It obtains blood from the frontal, parietal, & occipital superior cerebral veins, as well as the diploic veins.
Because of advancements in neurological imaging methods and therapeutic research, intracranial venous structures have piqued neurosurgeon attention. And the dispersion of the cerebral crossing vein & dural venous pool via the SSS isn’t as uneven as previously thought. [ Figure 3 ].
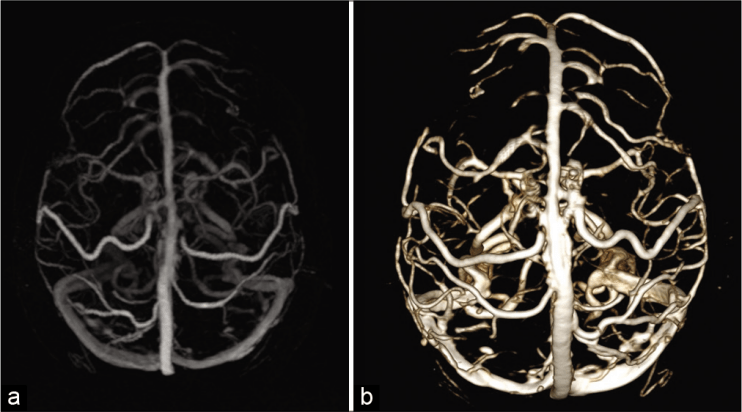
Figure 3: 3-D MRV (a) & volume depiction of MRV (b) in a healthy person exhibiting cerebral crossing vein draining in the superior sagittal sinus.
The majority of blood vessels (BV) drains into the superior sagittal sinusS at or around the coronal suture. Instead of approaching the dural sinus properly, they usually empty into dural venous pools.
These BVs, as well as dural venous pools, may provide a major barrier to surgical techniques to the parasagittal area. And throughout the entrance of the dura mater bordering the SSS & there may be unintentional damage regardless of great caution.
Injuries:
Cerebral BV injury throughout neurosurgical operations may cause a variety of neurological problems. Such as postoperative brain edema and ischemia, particularly when it comes in combination with brain protrusion and dural sinus blockage. This may lead to a more severe venous issue. As a result, these buildings require particular care.
Surgical Course of the superior sagittal suture
Among several other entry sites into the skull, the SSS is often discovered during neurosurgery operations for inter-hemispheric transcallosal methods. The opening of this dural venous sinus is mostly needed in the treatment of diseases around the falx & tentorium.
The control organizations are not accessible in several nations across the globe, although they are very helpful. The existing placement of the superior sagittal sinus at the outer cranial surfaces for appropriate supratentorial craniotomy placement as well as transoperative perspective is still dependent on cranial topographic anatomy investigations, particularly in cadaveric samples.
Even though the sagittal suture may be utilized as a crude exterior marker as well as to approximate the location of the underlying SUPERIOR SAGITTAL SINUS, it is not a precise landmark, as well as interruption of the superior sagittal sinus may result in severe problems.
As of the surgical difficulty, the neurosurgeon must determine the precise placement of the superior sagittal sinus.
Some scientific researches findings:
Tubbs et al. and Samadian reported comparable findings in cadaveric samples, and their investigations were conducted in the same way. This finding confirms that MRI is a trustworthy foundation of information.
The bulk of our measurements showed that the superior sagittal sinus deviates to the Rt-side of the middle. This is consistent with prior research. Furthermore, the superior sagittal sinus has a propensity to discharge to the Right transverse sinus in a dominating manner.
Due to the extreme possible danger of interrupting superior sagittal sinus and other crossing veins, we suggest which burr opening & drill machines be placed at min 1.7 cm apart from the sagittal midline, according to our results.
Utilizing the midline as a marker, Reis et al. evaluated the breadth of the superior sagittal sinus in cadaveric samples as well as in vivo patients utilizing MRIs. While these anatomical samples yielded comparable findings, the radiological sample yielded better findings.
This could be related to the MRI series. They employed to evaluate the superior sagittal sinus, while T1 isn’t the greatest for venous sinus assessment & measuring dimensions. And it may overstate the extent & movement of the SSS.
Blood supply and lymphatics of Superior Sagittal Sinus
The superior sagittal sinus empties both hemispheres of the brain as well as acts as a single midline venous system. And SSS is receiving blood from numerous emptying veins inside the cortical hemispheres.
There are many typical variations in the emptying vessels of the superior sagittal sinus, as well as the average amount of drainage vessels for every hemisphere of the cortex varies from 13 to 19. For every particular person, this number is about equal on both sides.
The vein of the Trolard, which links the superficial middle cerebral vein with the superior sagittal sinus, is the most important emptying channel of the SSS. A further important tributary of the superior sagittal sinus is the Rolandic vein, which empties the brain’s main motor and somesthetic sensory cortices.
As the SSS is located between the two dura mater leaves, the last emptying veins should travel across the subdural gap to approach it.
Bridging veins are the terminal emptying veins that play a critical role in the pathophysiology of subdural hematomas. There are numerous “emissary veins” which link the extra-cranial skull veins to the SSS, in contrast to the intracerebral tributaries.
Takeaway
Neurosurgeons ought to be informed that sagittal midline & sagittal suture aren’t dependable boundaries for the SSS path when doing neurosurgical procedures to the middle.
Also Read: Dural Venous Sinuses
FAQs
What does the SSS do?
The superior sagittal sinus (sometimes called the superior longitudinal sinus) is an un-paired region alongside the connected border of the falx cerebri in the human skull. It enables blood to flow to the convergence of sinuses from the lateral portions of the anterior cerebral hemispheres.
Does the SSS drain into the straight sinus?
The superior cerebellar veins & the inferior sagittal sinus both discharge into the convergence of sinuses, and the straight sinus takes blood from both.
Where does the superior sagittal sinus originate?
The superior sagittal sinus starts anteriorly, at the crista Galli of the ethmoid bone, and takes a vein called emissary from the nasal cavity via the foramen cecum of the frontal bone on rare occasions.
Does the superior sagittal sinus take blood away from the brain?
The SSS is the biggest of the venous sinuses, receiving blood from the superior cerebral veins of the frontal, parietal, & occipital lobes, as well as the diploic veins that connect with the meningeal veins.
What is the groove for the superior sagittal sinus?
A thin groove runs along the top border of the parietal, and, when combined with the grooves on the opposite parietal, creates the sagittal sulcus, a route for the superior sagittal sinus; the margins of sulcus provide connection to the falx cerebri.
What does the SSS consist of?
The falx cerebri’s connected boundary contains the SUPERIOR SAGITTAL SINUS. It originates in the foramen cecum and returns to the occipital bulge from where it meets the straight sinus (SS) & the LS to create the circular herophili.
What is contained within the superior sagittal sinus in a sheep brain?
Now look for the superior sagittal sinus, a rostro-caudally flowing venous area on the dorsal aspect that sits near the midline. This sinus gathers most of the hemisphere’s venous outflow and also serves as the entry point for cerebrospinal fluids into the vascular system.
Also Check: Complications of Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery