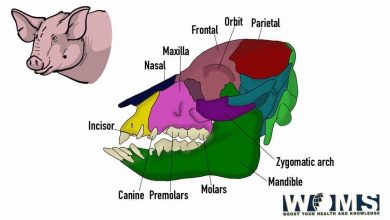
The ultimate guide to Lion Skull: Images and Anatomy
All of Africa is home to lions. Lion females lack a mane, in contrast to males. They also remain in the relatively similar category throughout their entire lifetimes, however, men often only do so for three to four years. A mature female lion inhabits the skull of this lion. The lion skull is in fantastic shape; both the color and the state of the dentition are outstanding.
Lion characteristics
Lions have been revered across history as representations of valor and sturdiness. These recognizable creatures have strong bodies—their size is only surpassed by tigers in the cat family—and roars that are audible five kilometers away. The coat of an adult lion is yellow-gold, while young lions possess a few light patches that fade with time.
Manes, the stunning fringe of long hair which surrounds animals’ heads, are normally only displayed by male lions. The African lion skull was very large. The savannahs and grasslands of sub-Saharan Africa are home to African lions. Because they spend about 20 hours a day sleeping or enjoying, they are the most gregarious of all cats and seem to prefer bodily connection.
In the wild, male lions rarely live longer than ten years; females can live up to 15 years. The African lion exists in feelings of pride made up of one or more adult males, one or more adult females that are linked to them, and their young. The mane, which only male lions have, is the animal’s most distinguishing characteristic.
The Lion Skull in brief
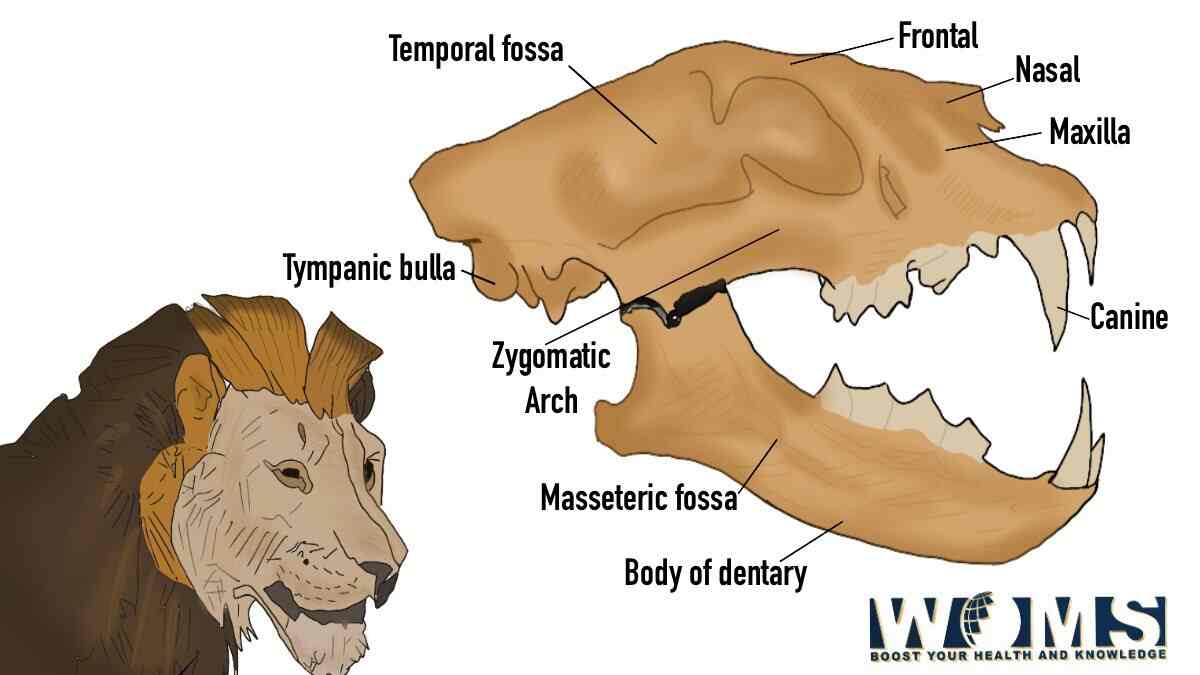
The dentition system and cranium of an African lion are the pinnacles of carnivore adaptation. Massive canines could readily compress windpipes and destroy spinal cords, while the back teeth would tear skin such as scissors. For optimal applied load, the longest blades are positioned posteriorly close to the joints as well as the muscles. The lion belongs to the Felidae family, which also includes other animals with retractable claws, a related dentition structure, and a general skull shape. The same presents with lion skull.
Although it belongs to the cat family, the cheetah is the only member without extensible claws. Panthera is the Latin word for leopard, and Leo is the Latin word for lion. This Lion skull demonstrates the lion’s small jaw and the numerous faces and muscular connections that permit a strong bite. The strong canine teeth are made to penetrate the victim deeply, whereas the carnassial teeth, which resemble scissors, could readily tear into both flesh and skin. The male African lion skull is a massive, thick, and impermeable structural masterpiece and environmental artwork that was deliberately built.
One of the most lethal and effective dentitions on earth is controlled by strong musculature which is housed and stabilized across the whole skull. This great predator’s skull has a large supraoccipital crest formation, big zygomatic arches, and a huge sagittal crest. Enormously developed, lions may quickly break bones and rip apart thick skin due to their large canines and back teeth (carnassials), which resemble the blades of a timber saw. The masseter and temporalis musculature, accordingly, have surface areas for connection due to the vast curvature on the back of the jaw and the tall coronoid processes.
What can we infer about lions’ histories from their skulls?
Individuals might not be aware of this, however lion skulls might reveal a great deal concerning their past. The main portion of a lion that isn’t coated in hair and flesh is its skull. Which makes it simpler to research and take account of how their skulls evolved. The way that lion skulls have evolved through the ages as a result of various ecosystems, habits, and predators make them interesting.
For instance, since lions consume deer rather than buffalo or giraffes, lions in India have slimmer skulls than lions in Africa. Geographic location also has an impact on the evolution of skulls; for example, lions that live on slopes possess cone-shaped lion skulls because their necks are less grown than lions that dwell near water sources.
There exist two distinct categories of lion skulls: African lions and Asiatic lions, whether individuals are investigating lion skulls. Since lions just couldn’t chew bones sufficiently enough to penetrate the bones into the marrow, Asiatic lions possess tiny teeth. Since lions are required to utilize their bigger teeth to crush apart difficult bones in big animals like giraffes or buffaloes, African lions possess teeth with stronger enamel coatings. We can forecast whatever would occur in years ahead whenever lions are introduced by knowing how well these animals’ skulls evolved across the period.
Structure of lion skull
The large, sturdy, and hefty bones which make up a lion’s skull are crucial because they safeguard the brain. Among the heaviest components of the lion skull is still the frontal bone, which also forms the forehead. This is because it must be capable of withstanding significant power without cracking, which could happen during combat or scavenging. The lion’s skull was made up of facial and cranial components. Extensive nostril apertures as well as an incomplete skeletal orbit are present.
There was no supraorbital foramen. Wide zygomatic arches were present. There was a significant longitudinal depression dorsally in the frontal area. The mandible seemed to have a powerfully excavated masseteric fossa and a good crest. It was a paired bone with movable articulation. The dental formula was 30 teeth, which included carnassial premolars, large canines, and short incisors.
Lion’s Distinct Modification
Because of their reflecting eyes, which give them excellent night eyesight but poor day eyesight, lions prefer to attack at nighttime. Additionally, lions have visual acuity, which allows them to precisely evaluate distances because both of their eyes are facing ahead instead of to the side. Although lions’ hearing is only somewhat superior to that of many animals, because lions could adjust their ears, lions may hear sounds up to one mile distant.
Because of their highly evolved ability of smell and the Jacobson’s Organ, which is located on the roof of their mouth, lions can identify both other predators’ carcasses as well as their own. They are likewise highly responsive to scent because they develop a larger nostril chamber (the space behind the nostril), which implies that there are more nerves present.
Lion skull vs Tiger skull
The lateral view image clearly illustrates the most obvious distinction between a Lion’s and a Tiger’s skull.
The face of the Lion skull (top) is raised and often shorter. The entire face of the Tiger skull, on the other hand, is tipped steeply downward and exhibits a spherical appearance.
Owing to the curved ventral border of the mandible as well as the tuberosity underneath the carnassial (m1) as reported by Boule, the Lion skull would roll front and backward whenever the skull and mandible are put properly on a smooth platform (1906). On the other hand, the Tiger skull will remain securely in position.
Advantages of lions
By preserving water supplies necessary for producing electricity and drinking water, ensuring food security, sequestering carbon to slow climate change, and defending community members from natural disasters, lion management promotes various ecological systems.
An identifying animal is a lion: Sustainable populations frequently associate with productive environments that generally offer a variety of advantages to different varieties of plants and wildlife in addition to human groups. Maintaining vital sources of water, promoting food security, reducing environmental issues, and building resilience to flooding and other weather-related catastrophes are all benefits of productive ecosystems.
With a deeper comprehension of ecological systems, which might assist researchers and populations acquire a variety of financing sources, sustaining lifestyles, environmental sustainability, and lions produce economical advantages and draw significant cash.
Conclusion
Owing to the existence of a high population of females in organized social systems, which allows larger males to just be capable of dominating breeding, lions are exceptional among cats in exhibiting significant differences between the sexes. The several characteristics regarding organisms as well as how animals previously existed in their natural surroundings that we can learn from animal skulls.
A few straightforward assessments of an animal’s skull can provide information about its diet, for certain if it was just a wild animal or a victim, as well as which systems were most crucial to its survival.
FAQs
Do lions possess a brain?
The tiger has a larger brain than the lion, leopard, and jaguar proportional to their largest skulls when utilizing cranial volume as a metric of brain size. In comparison to sub-Saharan lions, which have similar brain sizes, Asian lions have considerably smaller brains.
How resilient is a lion’s skull?
How Durable Is A Lion’s Head? A lion’s skull is constructed of bones that are massive, powerful, and broad. Among the thickest and sturdiest sections of their skull, the frontal bone, which forms their forehead, can withstand a significant amount of stress when they are battling or scavenging.
Can lions think more than cats?
In actuality, lions are the breed of big cats that is the smartest. Lions are capable of surpassing almost every feline in several challenge studies. According to scientists, the lion’s benefit above all other big cats is a sociable lifestyle, and intellectual capacity leads to greater mental abilities.
How thick is the skull of a lion?
All such lions have a maximum FMH of 14.06 mm (median: 12.56 mm, range: 11.10–14.06 mm). Based on this number as the dividing line between skulls with a theoretically typical aperture as well as others exhibiting FM stenosis, comparisons across confined and free lions were also made. Two lion skull samples were in captivity.