Innovations in Healthcare: Remote Patient Monitoring App Development Trends
The healthcare industry has seen rapid innovation and adoption of new technologies over the past decade. One central focus area is patient monitoring system development. So they can improve patient care while reducing costs. Remote patient monitoring (RPM) refers to using digital technologies to collect medical data from patients in one location and electronically transmit it to healthcare providers in a different location for assessment and recommendations.
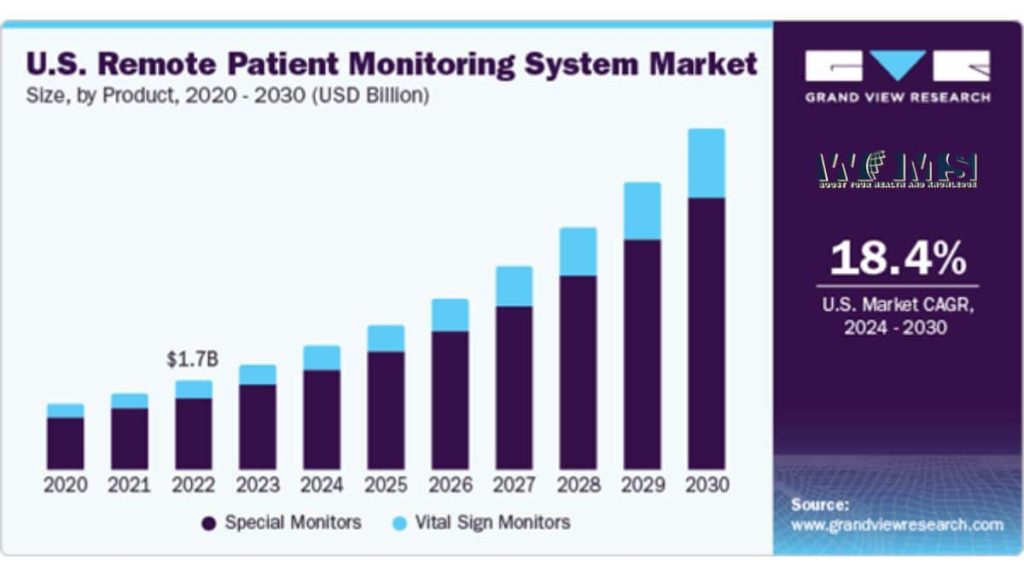
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the development and adoption of remote patient monitoring technologies and applications in patient monitoring systems. Providers and patients were forced to adopt telehealth and virtual care solutions during lockdowns and fear of virus exposure. Remote patient monitoring app development is becoming mainstream as patients and providers experience their convenience and effectiveness firsthand. Market research predicts the global remote patient monitoring market was estimated at $5.2 billion in 2023 and is expected to register a CAGR of 18.6% from 2024 to 2030.
As healthcare organizations look to capitalize on this growth, remote patient monitoring solution development company is focused on innovating in areas like:
Improving Interoperability Between Devices and Systems
A major challenge in launching effective RPM apps is managing interoperability between the vast array of patient monitoring devices like blood pressure cuffs, glucose monitors, ECG devices, and the software platforms they need to connect to. Issues like lagging networks, aging device fleets, and EHR integration threaten seamless data flows.
Empeek’s approach to building software has prioritized interoperability from the beginning. Starting remote patient monitoring software development with a reliable interoperability layer prevented huge problems down the line as the apps scaled to thousands of devices. Extensively testing devices and partnerships during development allowed the engineering teams to build out customized APIs to manage the unique data flow needs across providers.
Developing User-Centric App Design
Gaining user adoption among patients and providers has plagued many RPM app launches. Complicated interfaces, extensive onboarding procedures, lack of personalization, and poor ongoing support tend to hamper engagement.
Top app developers today prioritize creating easy-to-use, intuitive designs tailored to specific user needs. Features like SMS-enabled data flows require less troubleshooting from patients. Dashboards equipped with role-based controls streamline workflows for clinicians. And support channels like chatbots reduce the burden on IT teams. Design choices that make using RPM apps simple and frictionless promote ongoing utilization.
Incorporating Predictive Analytics and AI
Sophisticated analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms allow RPM apps to derive deeper insights from the vital sign data they collect. Beyond simply displaying readings like heart rate and oxygen saturation, these apps can analyze trends, detect anomalies, issue alerts based on algorithm-determined risks, and even predict adverse events. Modern apps are tapping machine learning to train predictive models on population health data. Cloud computing power allows models to continuously improve without impacting app performance. And automation reduces the need for clinicians to review and interpret every data point captured manually. The result is AI-enabled apps that effortlessly screen patients to identify those most at risk while providing support teams the information they require to react quickly.
Enabling Multi-Channel Communication
RPM apps must effectively support a web of communications between patients, providers, care teams, IT support, and other stakeholders. App architects looking to enhance connectedness focus on enabling multichannel outreach based on user preferences. Features like automated check-in calls and texts coordinated by chatbots improve patient engagement. Direct messaging allows clinicians to follow up on risks detected by the app easily. And native EHR integrations keep care teams up-to-date while helping manage documentation responsibilities.
Building flexible communication modalities tailored to individual preferences has been shown to drive better health outcomes in studies. Patients appreciate options like text-based interactions, while providers may favor more traditional emails and calls. Architecting RPM apps to seamlessly bridge these channel preferences while maintaining clear information flows is a priority.
Offering Customizable Sensor Options
The number of internet-connected health and wellness sensors on the market today is exploding. From smartwatches tracking exercise and sleep to blood glucose monitors and wearable ECG patches, consumers and healthcare providers have more data-tracking options than ever.
Savvy RPM developers are building sensor-agnostic platforms connecting this expanding monitoring device array to their apps. Modern architectures utilize cloud computing and APIs to build adaptable integration frameworks. As new sensors are approved and introduced, they can easily be tested and on-boarded to expand capabilities. This approach’s plug-and-play expandability allows RPM apps to scale across evolving industry and consumer needs.
Meeting Elevated Cybersecurity and Compliance Standards
Patient health data requires rigorous security and privacy standards to be met especially when this data is digitized and transmitted virtually, as with RPM apps. Developers must build compliant data governance procedures into app infrastructure. Features like access controls, user authentication protocols, encrypted data flows end-to-end, auditable actions, and strict regulatory-aligned policies must work together to provide accountability and protection.
Testing and assurance are critical in building trust with healthcare partners. Establishing clear validation reporting provides proof to customers that security controls are properly implemented and effective. Highlighting compliant infrastructure, testing procedures, and visibility into controls via external audits and attestations demonstrates an organization-wide commitment to cybersecurity when selling RPM solutions into healthcare.
Integrating with Telehealth Platforms
Many healthcare organizations invest heavily in telehealth infrastructure for video visits and virtual care. Savvy RPM developers are now working to integrate their apps more deeply with these telehealth platforms. Data flows directly into online visit workflows, powering remote exams with real-time patient vitals and trends. Alerts triggered within the app surface directly within virtual visit queues prioritizing clinician resources. Documentation protocols build closed-loop flows, automatically linking online visit notes to sensor data profiles.
Tightly coupling RPM apps and telehealth platforms aims to deliver more effective and efficient care while creating seamless clinician workflows. As telemedicine continues to rapidly mainstream adoption, developing these integrated capabilities ensures RPM apps will remain essential components of future virtual care ecosystems.
Conclusion
As remote patient monitoring becomes vital for modern healthcare service delivery, software innovators enable improved care through continual app improvements. Priorities like interoperability, intuitive design, smart data analytics, and sensor flexibility allow RPM apps to move care beyond hospital and clinic walls reaching patients wherever possible. Advances in communication channels, cybersecurity controls, and regulatory compliance build healthcare providers’ trust to scale these virtual health solutions safely. Organizations that invest in RPM app capabilities now will find themselves at the leading edge of healthcare’s data-driven future while making patient-centric care a reality today.