Otocephaly: A Rare Syndrome with Multiple Malformations
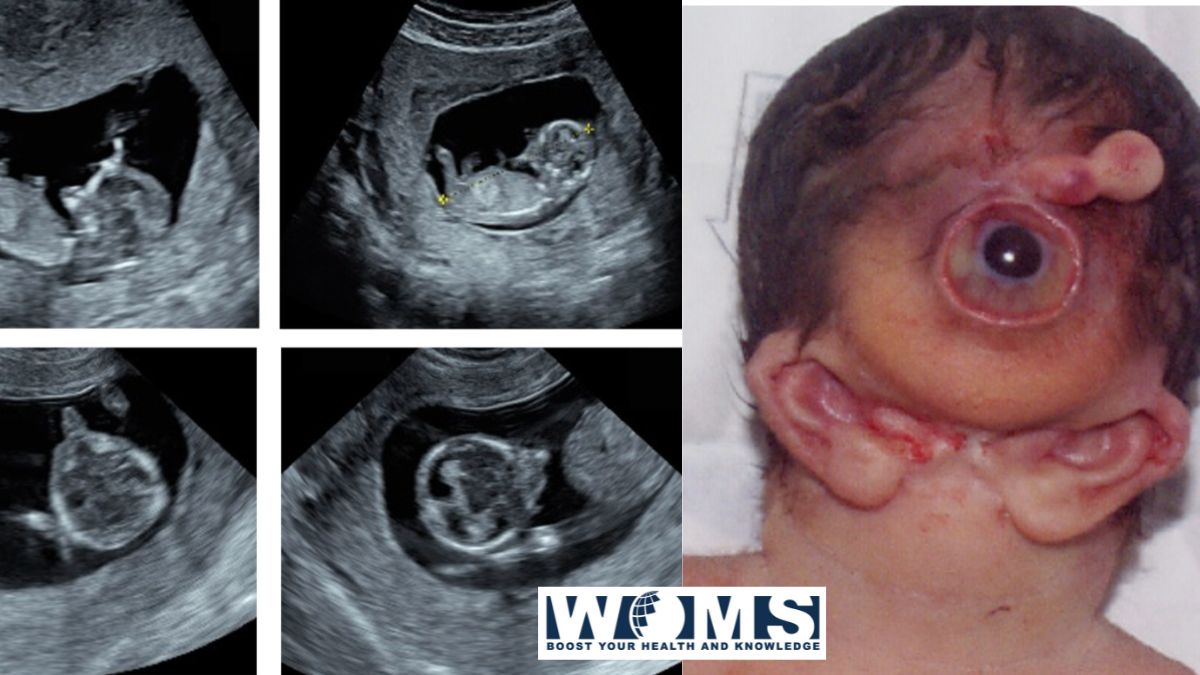
Otocephaly is a rare kind of syndrome associated with multiple malformations. The characteristic features include agenesis of the mandible (agnathia) or hypoplastic mandible, small mouth or microstomia, no tongue or rudimentary tongue (aglossia or microglossia), and anteromedial abnormal positioning of the ears (melotia). These malformations are mainly relevant to the ventral part of the first branchial arch. It usually arises due to the migration failure of the neural crest cells from the hindbrain.
These neural crest cells migrate from the hindbrain and induce the development of maxillary and mandibular prominences. These prominences start to develop at about the 4th and 5th week of the pregnancy. This article highlights the causes, prominent features, and pathological facts related to otocephaly. Continue reading the article to grab more details related to this syndrome.
What is the prevalence ratio of otocephaly?
Otocephaly is a rare syndrome, affecting only the minority of the population. The prevalence ratio of this syndrome is 1 in every 70,000 embryos. It is mainly because of the disturbance in the developmental patterns of the first branchial arch.
What are the signs and symptoms of otocephaly?
As we mentioned above, otocephaly presents with some characteristic features including:
- Agnathia or absence of the mandible
- Malotia or anteromedial position of the ears just below the level of the chin
- Aglossia or absence of the tongue
Besides these features, it also includes a variety of other signs and symptoms related to other structures of the body. These symptoms are as follows:
Facial or musculoskeletal changes
- Small mouth opening (microstomia) or absent mouth opening (astomia)
- Cyclopia with proboscis
- Median cleft palate with cleft lip
Neurological symptoms
- Holoprosencephaly
- Agenesis or malformation of the corpus callosum
- Neural tube defects
- Anencephaly
- Fully rotated internal organs (situs inversus)
- Cardiac abnormalities
- Ambiguous genitalia
- Absence of some glands
The grading system of otocephaly helps to differentiate the severity levels of this syndrome. It provides an easy way for physicians to treat such conditions. Sewall Wright explained twelve grading points in guinea pigs. These grades help to classify the symptoms according to the severity of the disease. The grading system is as follows:
- Grades 1 to 5 separate the embryo with agnathia (absence of mandible) without any neurological defects.
- Grades 6 to 9 explain severe holoprosencephaly.
- Grade 10 to 12 exhibit aprosopus (missing face and major portion of the head) with the complete absence of mesencephalon and prosencephalon.
There are reports of one human case presentation of an embryo with a high Wright grade in modern history.
What is the underlying cause of otocephaly?
Otocephaly is a rare syndrome arising mainly due to the de novo mutation in the PRRX1 gene at the long arm of the chromosome. Autosomal trisomies are usually common with medical problems like cyclopia. In contrast to this, it is quite rare. It is a developmental disorder leading to the disruption of the normal gestational period.
During early embryogenesis, different organs undergo developmental procedures. Disturbance in these procedures may cause malformation of these organs. The first branchial arch continues developing on the 23rd to 26th day of the normal pregnancy period. This is also known as the Carnegie stage. Failure to the normal developmental procedure may result in only agnathia. Otocephaly is a rare consequence of such mutations. Once the first branchial arch gets developed, there is no cure available to treat such problems.
To know more about Pregnancy and take care of yourself during pregnancy, you should check this free and awesome app called Pregnancy Journey App.
What are the possible management protocols?
This syndrome exhibits a variety of malformations of various structures. It ranges in severity from the severe micrognathia to the cyclopia-holoprosencephaly complex, which is usually lethal causing fetal death. It is classified into four major groups depending on the malformation of various structures. These are as follows:
- Agnathia
- Agnathia with holoprosencephaly
- Agnathia with situs inversus and visceral abnormalities
- Agnathia with holoprosencephaly, situs inversus, and visceral abnormalities
This syndrome also presents with different extracranial abnormalities including neural tube defects, corpus callosum dysgenesis, renal ectopia, adrenal hypoplasia, cephalocele, and rib, cardiac, and vertebral malformations.
The most severe cases are usually lethal and a fetus with otocephaly exhibits intrauterine growth retardation, premature birth, or disturbed ventilation. There are also severe airway malformations. For this reason, endotracheal intubation is difficult to restore airway passage. Only seven patients with non-holoprosencephaly survived beyond infancy.
The less severe cases, with mild agnathia, can be managed through extensive reconstructive surgical procedures. These procedures include the proper reconstruction of the mandible to follow proper face contouring. The lack of musculature is difficult to restore with such therapy but a reasonable life quality is achieved. Swallowing is quite difficult for such patients so enteral nutrition is provided. For all such cases, proper counseling of the family, premature birth planning, tracheostomy, initial gastrotomy, and long-term management plan are necessary for a quality cure of the symptoms.
Conclusion
Otocephaly is a rare syndrome associated with multiple malformations of the facial structures. It also includes extracranial changes associated with facial malformations. It is a developmental disorder arising due to a mutation in the gene. This genetic mutation causes disruption in the first branchial arch structures. It is quite a lethal syndrome with very few survival chances. There are also less severe cases of this syndrome that can be managed with reconstructive surgeries.
It is better to undergo some prenatal anomaly scans or diagnostic
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Is it possible to diagnose otocephaly before birth?
Prenatal diagnosis is quite difficult and rare. To date, there are more than 80 cases reported. The majority of the cases are usually found incidentally after the identification of other anomalies associated with otocephaly. A three-dimensional ultrasound is used to distinguish craniofacial features at the mid-trimester of the pregnancy. Magnetic resonance imaging also provides clear details regarding the facial and ocular abnormalities of the fetus
Do babies survive with otocephaly?
Otocephaly is a lethal syndrome reducing the survival rate of the affected babies. Babies that survive have to bear multiple challenges of reconstructive and rehabilitative procedures. The immediate management for such babies is a tracheostomy to secure the airway.