What Are the Dangers of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis?
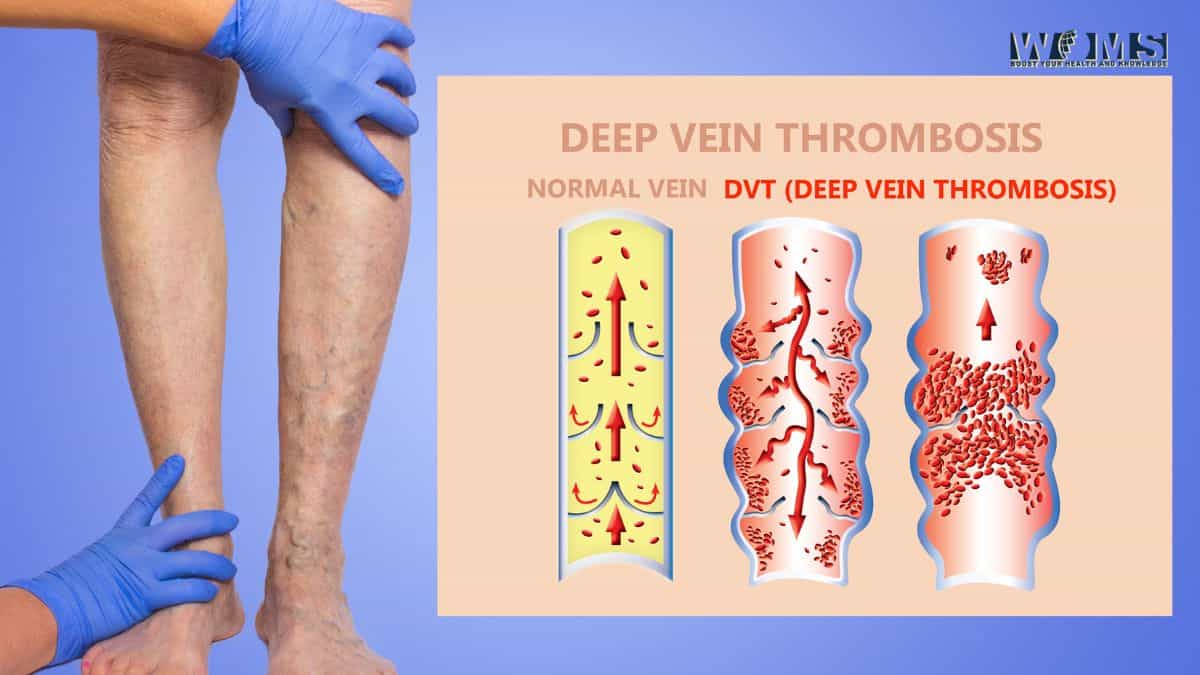
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition in which a blood clot forms in a vein, usually in the leg. DVT can cause pain and swelling, and if the clot breaks free, it can travel to the lungs and block blood flow; this is called a pulmonary embolism. DVT is serious and needs to be treated right away.
There are many risk factors for DVT, including prolonged immobility (sitting for long periods of time, bed rest), certain medical conditions (cancer, heart failure), pregnancy, smoking, and obesity. Symptoms of DVT include pain, swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected leg. If you think you may have DVT, it’s important to see a doctor right away.
Although DVT is relatively rare, it is estimated to occur in up to 600,000 people in the United States each year. The condition is most common in adults over the age of 40, and the risk increases with age. DVT is also more common in women than men. People with certain medical conditions, such as cancer or heart disease, are also at increased risk.
How is Deep Vein Thrombosis diagnosed?
DVT is diagnosed with a physical exam and imaging tests (ultrasound, MRI). Treatment typically involves taking blood thinners (anticoagulants) to prevent the clot from getting bigger and to reduce the risk of pulmonary embolism. In some cases, a filter may be placed in the vein to catch any clots that break free. Surgery is sometimes necessary to remove a large clot. With proper treatment, most people with DVT recover completely. Any good Dallas vein clinic should offer you the proper treatment for your deep vein thrombosis.
Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis
The symptoms of DVT can vary depending on the size and location of the clot. However, common symptoms include swelling, pain, and redness in the affected limb. In some cases, the skin may also feel warm to the touch. If left untreated, DVT can cause serious complications, including pulmonary embolism. Symptoms of pulmonary embolism can include shortness of breath, chest pain, and an irregular heartbeat. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
When a person has a blood clot, it can appear as a raised, red area on the skin that is warm to the touch. The person may also experience pain or tenderness in the area. In some cases, the blood clot may be visible just beneath the surface of the skin.
In more severe cases, the blood clot may be located deep within a muscle or organ, which can cause more serious symptoms. If a blood clot forms in an artery, it can block the flow of blood and cause a heart attack or stroke. If a clot forms in a vein, it can block the flow of blood and cause swelling, pain, and heat in the affected area. Blood clots can be dangerous and even life-threatening, so it is important to seek medical attention if you think you may have one.
Although DVT can occur without any symptoms, it can cause pain, swelling, and redness in the affected area. In some cases, DVT can lead to serious complications, such as pulmonary embolism. Pulmonary embolism occurs when a blood clot breaks loose and travels to the lungs, where it can block the flow of blood. This can be life-threatening.
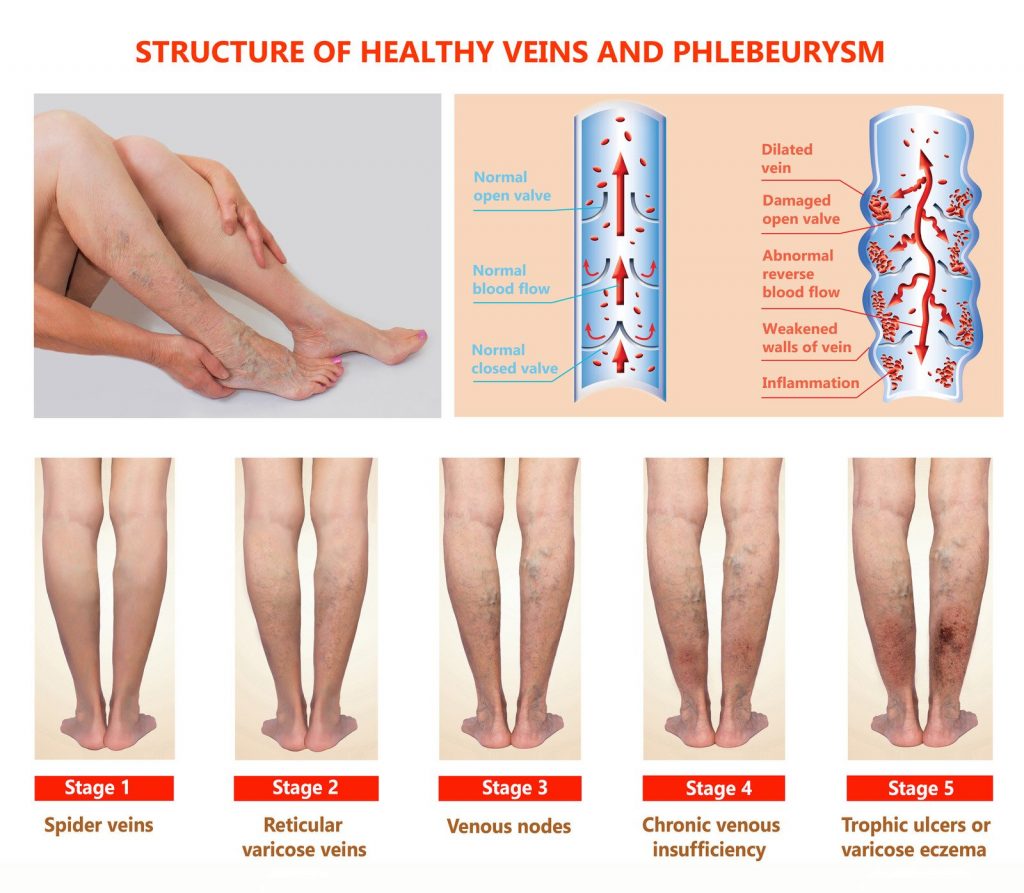
Other possible complications of DVT include post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS) and chronic venous insufficiency (CVI). PTS is a condition in which the veins do not function properly after a DVT. CVI is a condition in which the valves in the veins do not work properly, causing blood to pool in the veins. Both PTS and CVI can cause pain, swelling, and skin ulcers.
Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis is typically treated with anticoagulant medication, which helps to prevent the clot from getting larger and also reduces the risk of it breaking free. In some cases, a filter may be placed in the large vein that carries blood from the legs to the heart, to catch any clots that break loose. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the clot. With prompt treatment, most people with deep vein thrombosis fully recover.
How to prevent DVT?
Several measures can be taken to help prevent DVT, including regular exercise, loose-fitting clothing, and elevation of the legs when sitting or lying down. It is also important to avoid long periods of immobility, such as during long flights or car rides. If you are at increased risk for DVT, like if you have had it before or have certain medical conditions, your doctor may also recommend wearing compression stockings or taking blood thinners. By taking these precautions, you can help reduce your risk of developing DVT.