Itchy Pubic Hair: Causes And Treatments

Scratching the private region in public seems humiliating. Itchy pubic hair might be bothersome at first, particularly if it lasts longer than a short moment. During those times you might have the question of how to stop itching down there.
When someone has a severe irritation and doesn’t know what’s causing it, the individual should consult their health professional for adequate examination and treatment suggestions. The actual reason for itchy pubic hair will determine the medication. We’ll look at the cause, symptoms, treatment, and prevention of itchy pubic hair in this article.
Causes of Itchy Pubic Hair
There are various reasons for itchy pubic hair. These causes will help you with your answer to how to stop itching down there. Here are some causes of itchy pubic hair:
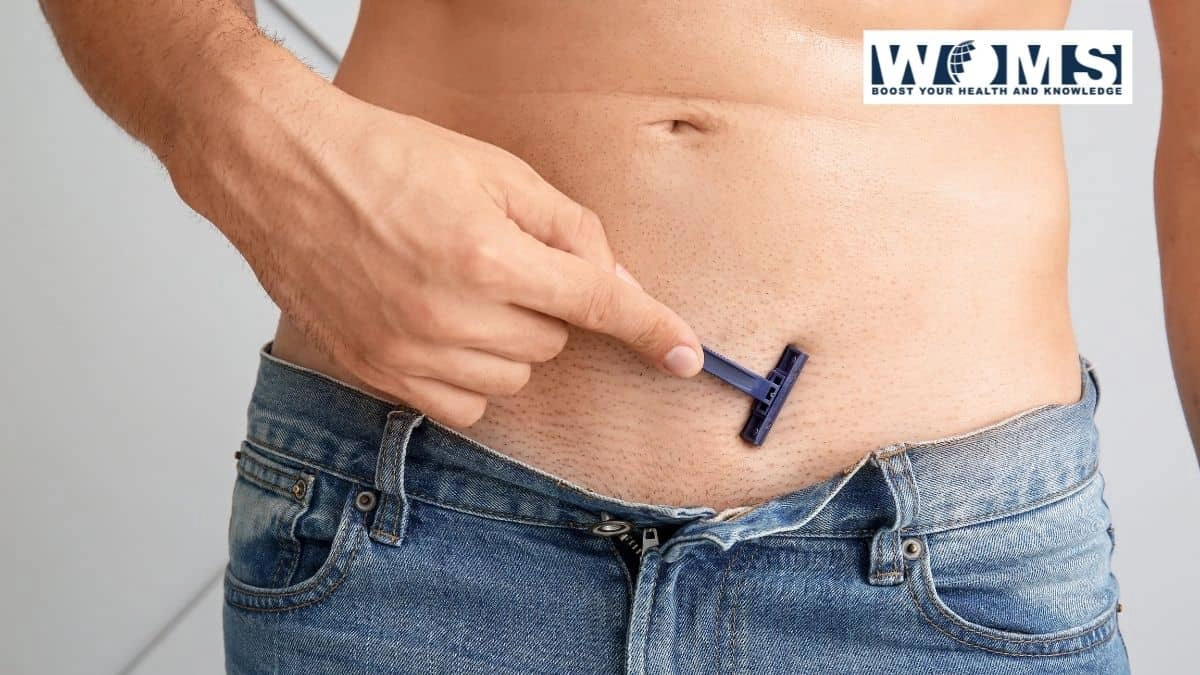
1. Razor Burn
Countless individuals experience itchy pubic hair or skin as a result of razor burn. When shaving the hairs in this spot, itching can occur, which can be exacerbated if a person shaves too quickly or with a dull blade. Razor burn is characterized by a reddish region of skin that is accompanied by sensitive red bumps and irritation.
Razor burn can be treated in a variety of ways. Irritation can be avoided by using suitable shaving procedures. Shaving with warm water to relax the hairline, using a sharp shaving blade, clipping longer hairs before shaving, using hypoallergenic shaving lotions or solutions, and shaving gently and evenly in the direction of the grain of the hair, rather than against it, all these are examples of good practices.
you should also know more detail about the question: Should women shave their faces?
2. Eczema
Eczema is another common cause of itching in the private parts. Eczema is mostly prevalent in kids under the age of five. Adults, on the other hand, are more likely to have recurrent versions of the disease. Eczema can resemble a variety of skin ailments. Most of the probable irritants are the same as those found in skin infections. Dryness, itching, and sensitive skin are common symptoms in areas of the body, including the groin.
Basic eczema treatments are over-the-counter lotions that can assist with itching and other symptoms. In the long run, using hypoallergenic items may help relieve discomfort.
3. Jock Itch
Tinea cruris, popularly known as jock itch, is bacterial pneumonia that causes itching in the upper thigh. Jock itch is fairly frequent and is most often found in wet, warm areas, such as a person’s groin after exercise. The spot may become red and itchy. A reddish, scaly layer of skin may develop in the area affected, causing severe itching.
Jock itch can be treated with a variety of over-the-counter antifungal topical creams. If these over-the-counter creams don’t work, stronger medical solutions may be able to eliminate the infection.
4. Skin Cancer
Some forms of skin cancer might induce irritation in the genital area, but this is an uncommon occurrence. Skin cancer in the cock or vagina can cause thick, red patches of skin that itch all the time. It’s possible that the skin will flow or drain, or that it will become more tender or vulnerable to bleeding.
A medical practitioner will conduct tests and laboratory findings to determine the best medical decisions for a patient with skin cancer.
5. Yeast Infections
When Candida, a commonly found fungi on the skin, overgrows on the epidermis, yeast infections arise. Infections with yeast are extremely prevalent. According to recent studies, 80% of all women will experience a genital yeast infection at a certain stage in their lives. Blistering in the genital area, as well as inflammation, bloating, burning, painful intercourse, discomfort while peeing thick, and white vaginal discharge are all usual symptoms of yeast infections. Several individuals benefit from using over-the-counter antifungal drugs to treat yeast infections. In other circumstances, stronger medical therapy is required.
6. Intertrigo
Inflammatory skin causes intertrigo. Intertrigo is a skin disorder that leads a red rash to emerge in wet parts of the body such as the skin folds, underarm, and genital area. Moisture and heat near the genital can lead to bacterial and fungal overgrowth. The rash may be black, extremely irritating, and have a bad odor.
Antibacterial and antifungal lotions are available over-the-counter to combat bacterial and fungal overgrowth.
7. Contact Dermatitis
The scientific word for itchiness caused by something irritating or causing an allergic reaction rubbing the body is contact dermatitis. Cleansers, coloring agents, or cloth, softeners in undies, perfumes or fragrances, additives in body wash, creams, or other beauty products, products a person uses, sexual lubricant, latex in condoms or gloves, and sanitary napkins are just some of the things that can cause contact dermatitis in the genital area and lead to itchy pubic hair. Other signs of dermatitis include hives, dry skin, and an itchy red rash.
Treatment
In some circumstances, avoiding an irritating product or piece of clothing may be the best remedy. Changing to a different detergent or solution may also help to alleviate discomfort. Antihistamines sold over the counter can help eliminate allergy symptoms. Anyone unsure about the underlying problem should get allergy testing from a dermatologist.
8. Increased Vaginal Discharge
During conception, the rate of vaginal discharge and cervical mucus you produce may rise. Hormonal fluctuations, as well as cervix and vaginal wall softening, produce this. Although discharge is intended to keep your vaginal area free of infection, it can inflame the vulva’s skin, leaving it dry and unpleasant.
9. Psoriasis
Lumps in the genital area and upper thighs are common in people with psoriasis. The National Psoriasis Foundation estimates that 35 to 70% of persons with psoriasis will develop genital psoriasis at some point in their lives. Even though the majority of patients with psoriasis acquire patches in other regions as well, some people’s first patches appear in the genital area. Itching and red, flaky skin are possible side effects.
Because of the tender skin in this spot, treating genital psoriasis can be difficult, but some therapeutic interventions include topical drugs, herbal remedies, ultraviolet B light therapy, and biologics (usually for people whose conditions do not respond to other treatments).
10. Pubic Lice
Pubic lice, often known as crabs, are microscopic parasites that suck on human blood and cling to hair for protection. Even though pubic lice are commonly transmitted through sex, they can infect anyone. This is because they can survive for up to 24 hours without a human host. The skin reacts to lice bites, causing chronic itching in the genital area. The individual may also feel irritated or tired. Small insects or tiny oval eggs may be discovered in the pubic hair or at the base of the hair. Both the bugs and the eggs can be difficult to see, necessitating the use of a magnifying glass.
Pubic lice can be treated with a variety of over-the-counter medicines, lotions, and conditioners. If these treatments are ineffective, stronger medical medications may be required. To eliminate any residual lice or eggs, people must remove the eggs and wash their bedding in the hottest setting possible.
11. Vaginal Dryness
Some women may have vaginal dryness during pregnancy as a result of hormonal changes. According to anecdotal data, women who are breastfeeding at the time of conception are more likely to have this discomfort. During intercourse, you may experience redness, inflammation, and pain. Some pregnant women may experience vaginal dryness as a result of low progesterone levels. If you develop this symptom, talk to your doctor because this hormone is required to keep a pregnancy going. Vaginal itching during pregnancy is usually nothing to be concerned about, and it can usually be treated at home.
How to Prevent/Avoid Itchy Pubic Hair ?
Preventive measures can go a long way toward assisting people to prevent itchy pubic hair in most cases of mild discomfort. Here are some suggestions for avoiding uncomfortable pubic hair.
Baking soda
Baking soda baths or baking soda treatments might help relieve itchy pubic hair.
Do not scratch the surface
Peeling an itch may provide temporary comfort, but it can also create more damage and inflammation in the area, making symptoms worsened. Scratching can also lead to other problems, such as wounds and infection.
Antibiotics
If you have a UTI, Sexually transmitted infection, or bacterial vaginosis, you’ll require prescription medicine.
Maintain a good hygiene
Cleaning the genital and body as a whole regularly can help avoid the development of some bacteria that irritate.
Cool water
Bathing in cold water and applying cold compresses to irritated pubic hair may also help.
Keep the area dry
After bathing, make sure the genital and pelvic area is completely dry. Wear loose-fitting, flexible textiles to facilitate airflow and thoroughly towel off after a bath or swim to achieve this. Avoid wearing damp clothing, such as swimming suits or gym clothes, for extended periods.
Avoid allergens
Changing to hypoallergenic cleansers, gels, and creams can help to alleviate allergy exposure and itchiness in the groin area.
Product elimination
If you believe your current cosmetics are causing your problems, try removing them entirely and replacing them with all-natural, gentle products meant for use during pregnancy or with babies.
Conclusion
Some causes of itchy pubic hair can be treated with simple home treatments. Others will require more intensive medical therapy as well as serious lifestyle adjustments to maintain control.
Preventative measures can go a long way toward preventing irritating pubic hair. Anyone who has symptoms that do not improve after trying home cures should contact a doctor for a complete diagnosis and treatment.
FAQs
What Causes Itchy Pubic Hair?
Hypersensitivity, jock itch, inflammations, yeast infection, and scalp psoriasis are all likely causes of genital irritation. Your doctor can assist you in determining the reason and recommending the best medication and preventative options.
Should I Worry About Itchy Pubic Hair?
It’s normally safe to scratch your pubic area. Call your doctor if the itching lasts more than a couple of days or is complicated by dermatitis or other signs. The indications could be caused by an infection or a more severe health problem.