Is Pneumonia Contagious after antibiotics?
Does pneumonia becomes contagious after using antibiotics?
Pneumonia is a disease of the lungs with a scope of likely causes. It tends to be a genuine and hazardous sickness. It typically begins with a bacterial, viral, or contagious contamination. In this article lets find out the Is pneumonia infectious after using antibiotics, chemical pneumonia, and bilateral pneumonia
The lungs end up excited, and the small air sacs, or alveoli, inside the lungs top off with liquid. Pneumonia can happen in youthful and robust individuals, yet it is riskier for more established grown-ups, newborn children, individuals with different sicknesses, and those with impeded insusceptible frameworks.
In the United States (U.S.), around 1 million individuals are treated in the healing facility for pneumonia every year, and approximately 50,000 bites the dust from the sickness.
Is Pneumonia Contagious after antibiotics?
When it comes to treatment antibiotics are most preferred to use. So, it normal to have a question Is pneumonia contagious after antibiotics?
When pneumonia patient is treated with the antibiotics -and started to feel better they can be still contagious for up to two weeks. in this case, the patient should be careful about the people around them. They can cover their mouth and sneezes, and exercise proper hygiene at all times.
The rising ubiquity of antibiotics resistance is to blame here. The antibiotics treatment may not always work because bacteria can develop resistance to the medications prescribed to the patients. this is also hard to detect the patient may start feeling better slowly, so they assume treatment works when really it should have worked earlier.
Read more about Antibiotic resistance
Moreover, in a healthy person whose body can very well fight off less significant bacteria, catching pneumonia from a person who’s on antibiotics is way less likely, a contrast to the odds for someone with a weakened immune system. the protection system in these individuals is compromised, so although they would ordinarily not get infected, they actually become quite ill. I hope you got an idea on Is pneumonia contagious after antibiotics.
Quick actualities on pneumonia
Here are some key focuses on pneumonia. More detail is in the principle article.
- Pneumonia is a disease of the lungs that can make a mellow extreme ailment in individuals everything being equal.
- It is the main source of death because of disease in kids more youthful than 5 years old around the world.
- Pneumonia and flu together are positioned as the eighth driving reason for death in the U.S.
- Those at high hazard for pneumonia incorporate more seasoned grown-ups, the specific youthful, and individuals with hidden medical issues.
Indications
- Pneumonia is a genuine lung disease with various conceivable causes.
- Pneumonia is genuine lung contamination with various conceivable causes.
- The main manifestations of pneumonia, for the most part, take over those on a cold or influenza. The individual at that point builds up a high fever, chills, and hack with sputum
Regular manifestations include:
- Corroded or green mucus, or sputum, hacked up from lungs
- fever
- quick breathing and shortness of breath
- shaking chills
- chest torment that typically intensifies when taking a full breath, known as pleuritic torment
- quick heartbeat
- exhaustion and shortcoming
- queasiness and heaving
- the runs
- perspiring
- migraine
- muscle torment
- perplexity or incoherence, particularly in more seasoned grown-ups
- shadowy or purplish skin shading, or cyanosis, from inadequately oxygenated blood
- Manifestations can differ contingent upon other hidden conditions and the kind of pneumonia.
- shadowy or purplish skin shading, or cyanosis, from inadequately oxygenated blood
- Manifestations can differ contingent upon other hidden conditions and the kind of pneumonia.
Causes of pneumonia
Microscopic organisms and infections are the primary drivers of pneumonia. Pneumonia-causing germs can settle in the alveoli and duplicate after an individual inhales them in.
Pneumonia can be infectious. The microscopic organisms and infections Those most in danger incorporate individuals who:
- are matured under 5 years or more than 65 years
- smoke tobacco, devour a lot of liquor, or both
- have fundamental conditions, for example, cystic fibrosis, ceaseless obstructive pneumonic confusion (COPD), asthma, or conditions that influence the kidneys, heart, or liver
- have a debilitated or impeded insusceptible framework, due, for instance, to AIDS, HIV, or malignant growth
- take drugs for gastroesophageal reflux malady (GERD)
- have as of late recuperated from a chilly or flu disease
- encounter ailing health
- have been as of late hospitalized in an emergency unit
- have been presented to specific synthetic substances or toxins
A few gatherings are more inclined than others to pneumonia, including Native Alaskan or certain Native American ethnicities.
Types
There are distinctive kinds of pneumonia, contingent upon their motivation.
Bacterial pneumonia: The most well-known reason is the bacterium Streptococcus pneumonia (S. pneumonia), yet various microorganisms can cause pneumonia Viral pneumonia: This can result from the respiratory syncytial infection (RSV) and flu types An and B, known as seasonal influenza Yearning pneumonia: This can happen when an individual inhales nourishment, fluids, or stomach substance into the lungs. This sort isn’t infectious.
Contagious pneumonia: This can result from a condition, for example, valley fever, caused by the Coccidioides growth. Healing center procured pneumonia: This can happen in patients being treated for different conditions, for instance, those joined to a respirator, or breathing machine. Notwithstanding the reason, the signs and indications will be comparable.
Avoidance
There are two distinct antibodies to avoid pneumococcal infection, the most well-known bacterial reason for pneumonia.
These cover a wide assortment of pneumococcal contaminations and are prescribed for the two kids and grown-ups, contingent upon their wellbeing conditions.
a pneumococcal conjugate antibody, or Prevnar
pneumococcal polysaccharide antibody, or Pneumovax
[vaccines can help secure against pneumonia]Keeping to an immunization timetable can help forestall contamination.
Prevnar (PCV13) is regularly included as a major aspect of a newborn child’s standard inoculations.
It is prescribed for kids under 2 years, grown-ups more than 65 years, and those between the ages of 2 and 64 years with certain medicinal conditions.
Pneumovax (PPSV23) is prescribed for kids and grown-ups who are at an expanded danger of creating pneumococcal diseases.
This incorporates:
- Grown-ups matured 65 years or more seasoned
- individuals with diabetes
- those with interminable heart, lung, or kidney sickness
- individuals who expend a lot of liquor or who smoke
- those without a spleen
- Those matured somewhere in the range of 2 and 64 years with certain other restorative conditions might be encouraged to have this antibody
The antibody may not totally shield more established grown-ups from pneumonia, but rather it can essentially lessen the danger of creating pneumonia and different contaminations caused by S. pneumonia), including blood and cerebrum contaminations.
Alongside inoculations, doctors suggest:
- normal hand washing
- covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sniffling
- shunning smoking
- eating refreshingly
- practising 5 days seven days
- avoiding the sputum or hack particles of others with pneumonia
A great many people recuperate from pneumonia in 1 to 3 weeks. Those in danger of extreme side effects ought to guarantee they keep up their inoculations.
Other types of pneumonia:
Chemical Pneumonia
Chemical pneumonia is known as lung irritation caused by aspirin or inhaling irritants. The irritants can be liquids, gases, and small particles, such as dust or fumes. The inflammation of the lungs in chemical pneumonia is due to viruses, bacteria, or poisons, or toxins. Though this pneumonia is not infectious but may cause severe irritation.
Symptoms of chemical pneumonia
Some of the symptoms of chemical pneumonia are:
- Dry cough
- Wet cough
- Haemoptysis
- Nausea or abdominal pain
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Headache
- Flu-like symptoms
Is chemical pneumonia contagious?
Pneumonia can be contagious after antibiotics because it is mainly caused by infectious microbes. But in the case of chemical pneumonia, it is caused by fumes, liquid, or other poisons not made by infectious, is not contagious.
Diagnosis of chemical pneumonia
The diagnostic criteria for everyone pneumonia are the same. You can read the diagnostic criteria above
Treatment of chemical pneumonia
The main aim of treatment is to inhibit the inflammation and to reverse it and reduce the symptoms affecting the individual. For reducing inflammation corticosteroids can be used. It should be used mostly before long-term scarring occurs. In the case of chemical pneumonia, antibiotics don’t prove to be helpful or needed, unless it is a secondary infection. In case of secondary infection, antibiotics can be used. Oxygen therapy may be helpful in chemical pneumonia.
Prevention of chemical pneumonia
You can prevent chemical pneumonia by following these measures:
- Maintaining personal hygiene like washing hands, especially after you go to bathroom and before eating foods.
- Have plenty of healthy fruits and vegetables in your diet
- Regular exercises
- Get enough rest
- Quit smoking
- Stay away from the sick people
Bilateral pneumonia
When both lungs of an individual are affected such a condition is called bilateral pneumonia. People who were exposed to flu or some streptococcal bacterial infection and other types of infection can develop bilateral pneumonia. Since it affects both lungs the person might feel difficult to breathe.
Symptoms of bilateral pneumonia:
It is hard to know a person has bilateral pneumonia by just looking at the symptoms. So, a person should consult a doctor as soon as they know it is pneumonia.
The symptoms of bilateral pneumonia are:
- People might have high fever with chills while some might have low temperature
- They might cough which worsen with time
- There is chest pain while coughing or breathing
- While doing activities you may feel shortness of breathing.
- There may be nausea or vomiting along with various respiratory symptoms
What causes Bilateral pneumonia?
It can be caused by microbes which causes pneumonia in both lungs. The main cause of bilateral pneumonia are:
- Bacteria: The bacteria is the common cause of pneumonia in the main adults. Streptococcus pneumonia is the bacteria causing most of the pneumonia cases in the United States.
- Virus: The virus causing most of viral pneumonia in adults is the influenza virus. While RSV is the most common virus causing viral pneumonia in very young children. It increases the chance of a person’s risk of developing secondary bacterial pneumonia.
- Fungus: It is a less common cause of pneumonia. A person with a compromised immune system is at a higher risk for fungal pneumonia compared to a person with a healthy immune system function.
- Other factors like age group nutrition and various other factors also cause bilateral pneumonia
When to look for the treatment?
Double pneumonia can prove to be life-threatening but it is also treatable. So it is necessary to look for the treatment early. So that it can be treatable before the infection establishes itself.
People having problems in breathing and high fever should seek for doctor and take it as an emergency.
People who have risk factors for pneumonia. They should seek medical care as soon as they experience symptoms of pneumonia.
With the help of tests like a chest x-ray and blood tests and physical examination from a doctor can know if an individual is suffering from pneumonia or not.
Risk factor
Pneumonia can affect anyone. But two age groups are at the highest risk:
- Children who are 2 years old or younger
- People who are age 65 or older
Other risk factor includes
- Being hospitalized
- Chronic disease
- Smoking
- Weakened or suppressed immune system
Treatment
Treatment relies upon the sort and seriousness of pneumonia.
Bacterial kinds of pneumonia are typically treated with anti-toxins.
Viral kinds of pneumonia are typically treated with rest and a lot of liquids. Antiviral drugs can be utilized in flu.
Contagious sorts of pneumonia are normally treated with antifungal drugs.
Specialists normally recommend over-the-counter (OTC) drugs to help deal with the side effects of pneumonia. These incorporate medications for decreasing fever, lessening a throbbing painfulness, and smothering hacks.
Also, it is vital to rest and drink a lot of liquids. Remaining hydrated disperse thick mucus and bodily fluid, making it simpler to hack up.
Hospitalization for pneumonia might be required if indications are particularly awful or if an individual has a debilitated invulnerable framework or different genuine diseases.
In the healing center, patients are commonly treated with intravenous anti-infection agents and liquids. They may require a supplemental oxygen supply.
In youngsters
In most youngsters, the resistant framework can shield them from pneumonia. On the off chance that a tyke develops pneumonia, it is more often than not because of an infection.
Indications include:
- trouble relaxing
- not nourishing appropriately
- fever
- fractiousness
- lack of hydration
Little children may whine of agony in their chest, and they may upchuck in the wake of hacking.
Treatment incorporates a lot of rest and a normal admission of liquids. The specialist may recommend over-the-counter for stomach issues, yet hack medications won’t help. Grown-ups ought not to smoke around kids, particularly in the event that they have pneumonia.
Finding
A specialist will get some information about side effects and restorative history and will do a physical examination.
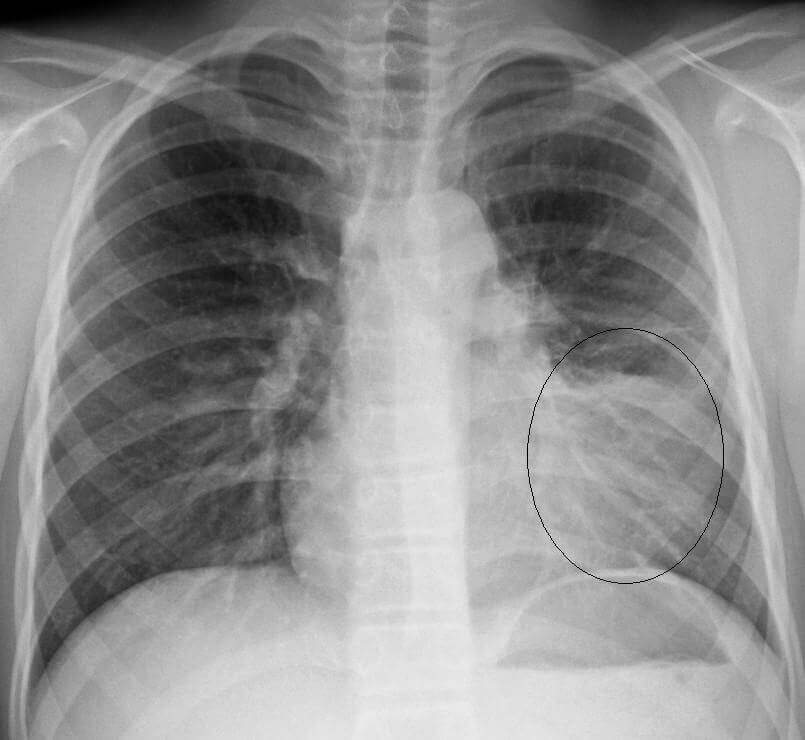
[lung X beam for pneumonia diagnosis]An X-beam can appear if there is any harm to the lungs.
They may presume pneumonia in the event that they hear coarse breathing, wheezing, snapping, or diminished breath sounds when tuning in to the chest through a stethoscope.
The specialist may likewise check the oxygen levels in the blood with an easy screen on the finger called a heartbeat oximeter.
Chest X-beams can affirm a pneumonia conclusion and show which regions of the lungs are influenced.
A CT sweep of the chest may give progressively point-by-point data.
Blood tests measure the white platelet check.
This decides how extreme the disease is, and whether a microscopic organism, infection or growth is the possible reason.
Blood societies may uncover whether the microorganism from the lungs has spread into the circulation system.
A blood vessel blood gas (ABG) blood test may give an increasingly precise perusing of the body’s oxygen and carbon dioxide levels and different elements.
A sputum examination can figure out which life form is causing pneumonia.
A bronchoscopy is some of the time utilized for further examination.
A thin, adaptable, and lit cylinder called a bronchoscope is passed down into the lungs. This empowers the specialist to look at straightforwardly the tainted parts of the aviation routes and lungs. The patient is under soporific.
Complications
Even after treatment, some people with pneumonia, especially those in high-risk groups, may experience complications, including:
- Bacteria in blood stream (bacteremia)
- Difficulty breathing
- Fluid accumulation around the lungs (pleural effusion)
- Lung abscess
Prevention
To help prevent pneumonia
- Get vaccinated
- Make sure children get vaccinated
- Practice good hygiene
- Don’t smoke
- Keep your immune system strong
Summary:
Pneumonia is an acute respiratory sickness associated with currently matured radiological pulmonary shadowing. That may be segmental, lobar, or multilobar. the context in which pneumonia develops is highly suggestive of the likely organism; therefore pneumonia is usually classified as community- or hospital-acquired or those occurring in immunocompromised hosts.
Is pneumonia contagious after antibiotics? yes, it can be contagious to other people around the pneumonia patient. so pneumonia should follow some of the healthy ways to make safe people around them. I hope this article helped to know about the Is pneumonia contagious after antibiotics? If this article helped you regarding Is pneumonia contagious after antibiotics? then do share this information.
Do read Pulmonary Toilet.