The Submental Triangle
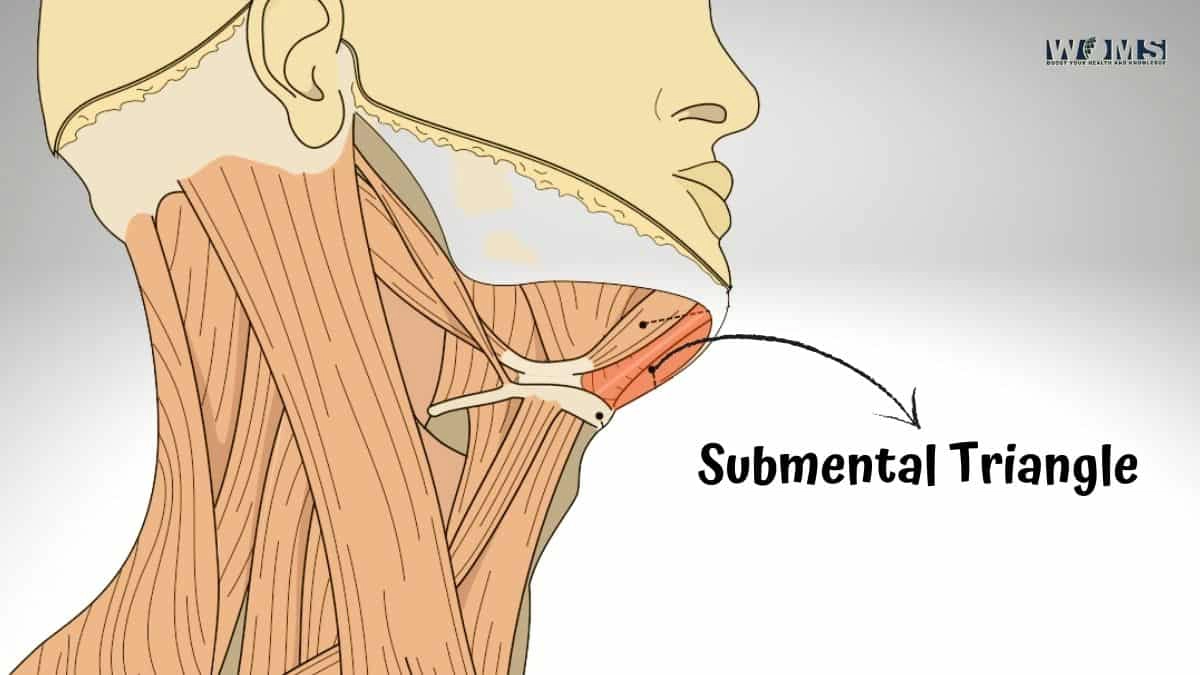
The Submental Triangle is a small triangular area of the neck that lies below the chin and above the anterior part of the neck. It has three borders: an inferior border, a superior border, and a lateral border. The inferior border is formed by connecting line points where two muscles meet on either side of this region: sternocleidomastoid muscle and digastric muscle from the other.
The superior border is formed by a line connecting the mastoid process (a bony bump on the skull behind the ear) with the hyoid bone (a horseshoe-shaped bone that sits at the base of the tongue). The lateral border is formed by a line connecting two points on either side: halfway between the angle of the mandible and the mastoid process and halfway between the hyoid bone and Adam’s apple.
Boundaries of the Submental Triangle
On the sides, it’s bounded by anterior belly digastric muscle laterally and hyoglossus medially. Sternocleidomastoid muscle also helps to bound posteriorly its boundaries on the side where it overlaps with the suprahyoid region. And if we go over inferiorly, then geniohyoid runs at whereas genioglossus runs at.
The submental Triangle is a small, triangular region of the neck bounded by the anterior belly of the digastric muscle laterally, the hyoglossus muscle medially, and the sternocleidomastoid muscle posteriorly. The inferior boundary is defined by the geniohyoid and genioglossus muscles.
The posteroinferior border of the mandible serves as its base, while the superior aspect of the mylohyoid line forms the upper boundary. The lower margin is at a level with a lower edge of inferior constrictor muscle. Boundaries
Anterolaterally – angle or coronoid process bodies Mentalis muscles from below Mentum Posteromedial – Submandibular gland Lymph nodes Medial to sternocleidomastoid are the internal jugular vein and carotid sheath.
Relations of the Submental Triangle
The following share a relation with the submental Triangle:
Submental Triangle is a geometric area of the anterior neck that lies directly below the chin. It includes two triangles called ‘submental’ and ‘submandibular.’ The main boundaries of this region are sternocleidomastoid muscle superiorly, mandible inferiorly, midline medially, and mental nerve laterally.
Functions of Submental Triangle This triangular space separates the lower lip from skin overlying jawline angles to create an elliptical opening with a vertical axis for dental occlusion during mastication. Upper limit: Lateral border of the body of mandible Lower Limit: Anterior margin or mylohyoid line Medial boundary: Midpoint between symphysis menti and hyoid bone.
Linguo-Facial Region Diagrams The submental Triangle lies just below the chin and is separated from the suprahyoid muscles above it by a sheet of fascia known as the platysma.
The submental Triangle is a small region divided into two smaller triangles, the anterior and posterior triangles. The boundaries of the anterior Triangle are as follows: Superiorly – mandible Inferiorly – the body of hyoid bone Anteriorly – midline laterally- mental nerve Posterior Triangle.
Contents of the submental Triangle
The submental Triangle contains several important structures:
- The hypoglossal nerve (cranial nerve XII) passes through it on its way to supply the tongue.
- The facial artery and vein cross over it on their way to the face.
- The mylohyoid and geniohyoid muscles are located in this area and play an important role in tongue movement.
- The submandibular gland is located in the deep part of the Triangle.
- The lingual nerve and chorda tympani branch of the facial nerve passes through it on their way to the tongue.
- The cervical lymph nodes are located in the deep part of the Triangle.
- The mental nerve passes through the mental groove on its way to innervate the chin.
The submental Triangle is important for several reasons:
- The submental Triangle is an easy area to palpate for abnormalities such as lumps or swelling.
- The submental Triangle is a useful landmark for performing certain medical procedures.
- The submental triangle can be used to measure the depth of anesthesia during surgery.
- The submental Triangle is an important region for cosmetic procedures such as liposuction or neck lift surgery.
- It’s an easy area to palpate for abnormalities such as lumps or swelling.
- This region is also a useful landmark for performing certain medical procedures.
- Furthermore, it can be used to measure the depth of anesthesia during surgery.
- Finally, this part of your neck is important in cosmetic procedures like liposuction or neck lift surgery.
Superficial and Deep Contents of Submental Triangle
The superficial and deep contents of the submental Triangle are as follows:
Superficial contents of the submental Triangle are muscles that form the boundary between it & the suprahyoid region, whereas deep contents contain the Submandibular gland, facial artery, lymph nodes in the cervical chain
The deep contents of the submental Triangle are the following structures: The submandibular gland, facial artery, lymph nodes in the cervical chain, and mental nerve in the mental groove. And there is a Mylohyoid muscle that forms the boundary between superficial & deep parts of this Triangle. On the sides, it’s bounded by anterior belly digastric muscle laterally and hyoglossus medially. Sternocleidomastoid muscle also helps to bound posteriorly its boundaries on the side where it overlaps with the suprahyoid region. And if we go over inferiorly, then geniohyoid runs at whereas genioglossus runs at.
Innervation and Blood Supply to the Submental Triangle
The submental Triangle is innervated by the mental nerve (CN XII), which provides sensory innervation to the skin of the chin and lower lip. The main function of this region is to create an elliptical opening with a vertical axis for dental occlusion during mastication. This space also allows the passage of food from the mouth into the pharynx.
The facial artery supplies the submental Triangle. The skin of this region is very vascular, which makes it ideal for injection of local and ales esthetics or lip augmentation fillers such as hyaluronic acid.
The submental Triangle is a region of the neck located below the chin. This area is innervated by the mental nerve, which provides sensory innervation to the skin of the chin and lower lip. The main function of this region is to create an elliptical opening with a vertical axis for dental occlusion during mastication. This space also allows the passage of food from the mouth into the pharynx.
Lymphatic Drainage of the Submental Triangle
The submental Triangle houses lymph nodes that drain structures in the head and neck, such as the parotid gland, submandibular gland, and anterior portion of the tongue. These nodes can be palpated by gently pressing downwards on either side of the chin below the lower lip. The nodes are arranged in a triangular fashion, with the apex of the triangle pointing towards the midline.
The submental Triangle is drained by two major lymphatic vessels: the deep cervical lymphatic trunk and the jugular-subclavian lymphatic trunk. The deep cervical lymphatic trunk drains lymph from structures in the upper neck, such as the thyroid gland, while the jugular-subclavian lymphatic trunk drains lymph from structures in the lower neck and chest, including the heart and lungs.
Division of the Submental Triangle
The submental triangle can be divided into an anterior and posterior portion by drawing a line between two points: (i) midway between the mandible and hyoid bone; and (ii inferior to the cricoid cartilage. The anterior portion is bounded by the platysma muscle, medially by the mylohyoid muscle, and inferiorly by the hyoglossus muscle. The posterior portion is bounded laterally by the trapezius muscle, medially by the sternocleidomastoid muscle, and superiorly by the omohyoid muscle. The anterior and posterior portions are joined by the midline of the neck that consists of the median line, jugular furrow, and submental crease.
A submental triangle is a well-protected place in the neck. It is located behind the beard and in front of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The anterior portion has many important structures: the facial nerve, mylohyoid nerve, hypoglossal nerve, and lingual artery. The posterior portion has the carotid sheath, which contains the common carotid artery and internal jugular vein. Other important structures are present in this area, such as lymph nodes and ducts. For these reasons, it is very important to protect this area when undergoing any surgery or procedure in the neck region.
The importance of the Submental Triangle
The importance of submental triangle of the neck cannot be overstated. It is a key area for both protection and health. The submental Triangle is located below the chin in the lower part of the neck. It is bounded by the sternocleidomastoid muscle (SCM), the platysma muscle, and the digastric muscle.
Submental triangle is an important protective zone. The SCM and platysma muscles are powerful muscles that can tense up quickly to protect against blows or other injuries to the head and neck. The digastric muscle helps to stabilize the jaw and skull.
Submental triangle is also an important health zone. The lymph nodes in this area help filter out toxins and bacteria from the blood. The submental Triangle is one of the few areas where lymph nodes can be easily accessed for examination or biopsy.
The submental triangle is a key area for both protection and health. It is an important part of the neck that should not be overlooked.
Also Check: Triangle of Auscultation
Clinical Importance of the Submental Triangle
Here is the clinical importance of the submental Triangle;
The submental Triangle is an important clinical area because it receives its blood supply from the facial artery (a branch of the external carotid artery which supplies most structures in the face. It contains two major vessels; inferiorly, this Triangle is related to the facial vein and superiorly to the internal jugular vein. Because of that reason, there may be a risk for injury if you do not take care while shaving or performing any other treatments in these areas. Submental triangles are also clinically significant because they can result in hematoma formation after surgery performed under general anesthesia. These regions lack overlying muscle tissue protecting them against inflammation caused by instruments placed within their boundaries. That’s why your surgeon will tell you about postoperative steps so that you can maintain a clean environment and avoid any sources of infection.
The course of the Facial Artery in the Submental Triangle
The facial artery travels through the submental Triangle, starting from the lower border of the mandible and running medial to the submandibular gland. It then pierces the deep cervical fascia and enters the platysma muscle. The artery then travels superficially in front of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, lying on the carotid sheath. It is important to be aware of this course when performing a neck dissection as it is easily injured during surgery.
Injuries to the Facial Artery
The most common injury to the facial artery occurs during thyroid surgery. The artery can be injured by retractors or by transecting it with electrocautery. Other injuries can occur during neck surgery or trauma, such as lacerations from a knife or bullet. If the facial artery is injured, significant bleeding can occur. This can be a life-threatening injury, and prompt surgical intervention is required. The submental Triangle is a safe place to perform surgery as it is well away from the course of the facial artery. This allows for a safe dissection of the neck without the risk of injuring this important vessel.
Blood Supply to The Submental Trianglelood supply to the submental Triangle is via the submental and carotid arteries. The submental artery is a branch of the facial artery, which is a branch of the external carotid artery. The carotid arteries are two large blood vessels that supply oxygen-rich blood to the brain. The Submental artery is a vessel that arises from either the exterior or interior of the facial artery. It is usually found in about fifty percent of cases and travels inferiorly to the hyoid bone, where it divides into two branches: anterior auricular and posterior auricular.
In terms of deep structures within this region, many important anatomical boundaries are formed by various muscles that occupy small spaces between themselves. These regions tend to be areas for potential infections or tumors as they have limited access to blood supply coming from surrounding tissue. This area also contains some lymph nodes at times compared to other locations on the body, such as those located alongside bellies (axilla). The submental Triangle has been noted historically for its ability to absorb iodine when given orally, making this area very well suited for radiation therapy.
Location about Other Regions of the Neck
Anatomically, many important boundaries are formed by these structures, which reduces their ability to be accessed easily for nearby vessels supplying them with needed oxygen-rich blood; instead, most absorb minerals like iodine better than any other part of
Anatomical locations within this region are important because they are formed by muscles that occupy small spaces, making it difficult to access blood supply from surrounding tissue. The submental Triangle is an excellent location for radiation therapy because it absorbs iodine very well when administered orally. This small area also contains few deep lymph nodes compared to other body regions, making it relatively safe from potential infection or tumor growth.
Also Read: Posterior Tibial Artery
Conclusion
The submental Triangle also alluded to as the suprahyoid Triangle, is an unpaired suprahyoid region that is mediocre compared to the jawline.
They add to the mylohyoid line of the mandible and run medially and descend to append to the body of the hyoid bone. The submental Triangle harbors the submental lymph hubs that channel the psychological district, the tip of the tongue, mediocre lip, and incisor teeth.
The submental Triangle is a shallow district; it houses some significant designs, for example,
the mylohyoid nerve, lymph organs, a few little lymph hubs called submental lymph hubs, and some little veins which join in shaping the foremost jugular vein.
FAQs:
What are the contents of the Submental triangle?
The Submental Triangle contains two lymph glands, the submental lymph nodes, Submental veins, and commencement of anterior jugular veins.