Serum vs Plasma: A Dossier
It’s not uncommon for people to get confused about serum vs plasma. These two terms are often used interchangeably, but there is a difference between the two.
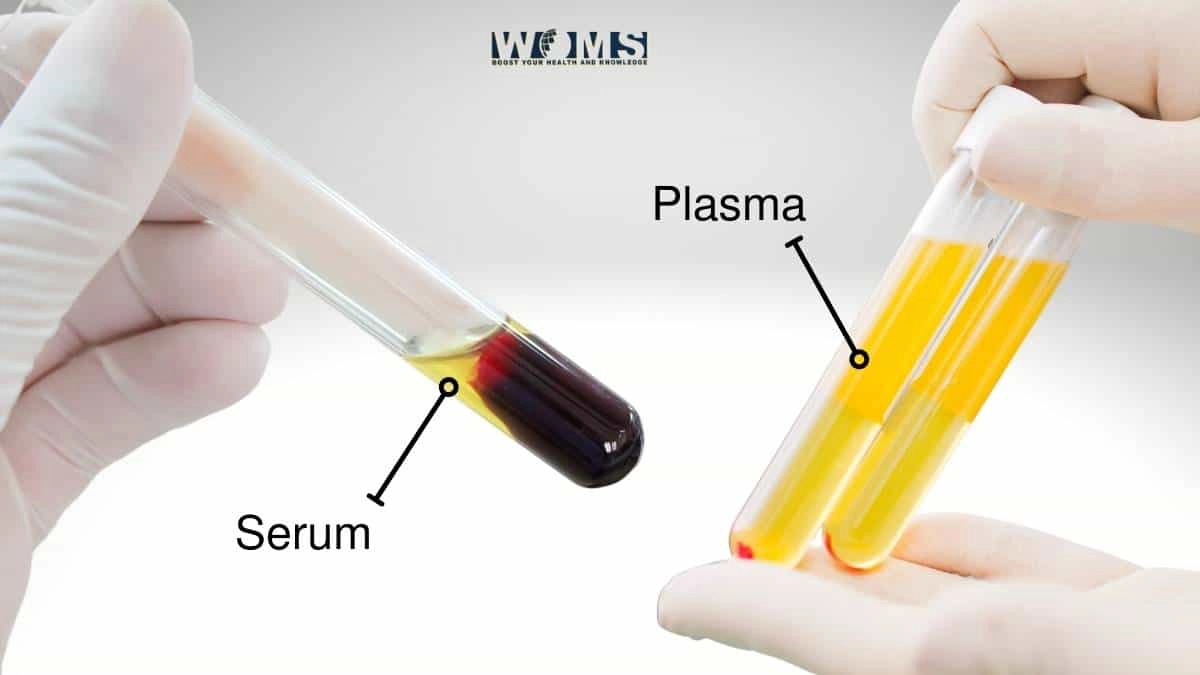
Serum refers to blood serum, which is essentially what remains of whole blood after clotting has occurred.
Serum
The serum is a yellowish fluid that remains after blood has been allowed to clot and the cells and fibrin removed. It consists primarily of serum albumin, globulins (antibody proteins), clotting factors (such as thromboplastin), fatty acids, hormones, salts, glucose, amino acids, urea nitrogen waste products such as creatinine; it also contains tissue plasminogen activator.
The serum is the part of blood that remains after clotting is mostly water but contains dissolved gases, nutrients like glucose, and other proteins. Its major function is to transport soluble materials around the body while maintaining osmotic pressure.
This makes sense because we’re always losing some ions through our skin in sweat, etcetera; if this weren’t maintained properly throughout our bodies, then fluids would move to one area or another based on where they were most concentrated rather than being maintained at a constant
Importance of serum
The most common use for serum in medical treatments is an intravenous drip containing iron and other nutrients needed by the body during prolonged periods of illness or injury.
Plasma
The red color results from oxygen being bound to iron atoms in our blood cells. Plasma makes up an impressive 55% of your total blood volume and contains dissolved ions, proteins, sugars, and lipids. It also serves as a transport system for water-soluble nutrients like glucose.
In comparison with serum,
Plasma has many more protein molecules within it. Once you separate all the cellular components (including platelets ) from whole blood, what remains will be approximately 92 percent liquid phase or about 88 percent interstitial fluid plus about four percent plasma which makes 94 percent of total body water
- The serum is a clear yellow liquid that remains after clotting has occurred
- The most common use for serum is intravenous drips.
- Plasma is made up of water and proteins.
- The primary use for plasma is in blood transfusions.
- Plasma can also create therapies that help fight infections or cancers.
Plasma has no relationship with any form of bodily fluids because it only consists of water and proteins such as albumin and immune globulins (antibodies).
The primary use for plasma is in blood transfusions, as it helps maintain the correct balance of electrolytes and minerals in the body. Plasma can also create therapies that help fight infections or cancers. It’s important to understand the difference between serum and plasma so you can make informed decisions about your health.
What are the differences between serum vs plasma?
The differences between serum vs plasma are:
- Plasma is the more common term, but serum technically refers to any fluid that isn’t blood (i.e., lymph). And because “a lot of different body fluids can be classified as serums,” according to one source, it’s best not to use this word casually; instead, we recommend sticking with plasma or simply writing about both individually. That said, there are some differences between these two biological materials: first off, while they’re both derived from blood cells (and thus oxygenated), each has its unique chemical makeup.
- Serum vs plasma. Secondly, plasma tends to have a higher concentration of proteins than serum; in fact, one study found that the average protein concentration in human plasma was about twice as high as in serum. This means that if you’re looking for a boost in protein intake, drinking plasma may be more beneficial than sipping on serum. However, it’s important to note that not all proteins are created equal: while some (like albumin) are found at high concentrations in both serum and plasma, others (like immunoglobulins) are more abundant in serum.
- Serum vs plasma serum protein concentration. Finally, one of the key differences between these two substances is that serum lacks clotting factors while plasma contains them. This means that if you need to stop a bleed fast, using plasma as a topical treatment will be more effective than using the serum. Of course, in most cases, you won’t have to worry about which one you’re using–but now you know the difference just in case!
Each has its unique chemical makeup, while they’re both derived from blood cells (and thus oxygenated). Plasma tends to have a higher concentration of proteins than serum; in fact, one study found that the average protein concentration in human plasma was about twice as high as in serum.
This means that if you’re looking for a boost in protein intake, drinking plasma may be more beneficial than sipping on serum. However, it’s important to note that not all proteins are created equal: while some (like albumin) are found at high concentrations in both serum and plasma, others (like immunoglobulins)
Another difference between serum vs plasma
Plasma and serum are two different components of blood.
- Plasma is the liquid component, while serum is the protein-rich component.
- They have different functions in the body: plasma transports nutrients and oxygen to cells, while serum contains antibodies that fight infection. The serum also contains clotting factors that help to stop bleeding.
Blood components in the body that transport nutrients and oxygen to cells contain antibodies for fighting infection contain clotting factors that help stop bleeding. Blood liquid component consists of proteins and other substances in a water base. Serum protein-rich fluid is produced by blood when it clots or separates into two layers.
- Plasma transports nutrients and oxygen to cells, while serum contains antibodies for fighting infection; its ability to contribute to coagulation effectively stops bleeding from injuries.
There is a small amount of plasma in serum and a small amount of serum in plasma. However, the two substances have different properties that make them important for the body.
Plasma is essential for transporting nutrients and oxygen to cells, while serum contains antibodies that fight infection.
The serum also contains clotting factors that help to stop bleeding. If you are injured, it is important to have both plasma and serum present in your blood to heal effectively.
What is the main difference between them?
The main difference between them is that serum contains no clotting factors–so you cut yourself and need a quick fix? Plasma’s your go-to. Secondly, plasma tends to have a higher concentration of proteins than serum; in fact, one study found that the average protein concentration in human plasma was about twice as high as in serum.
This means that if you’re looking for a boost in protein intake, drinking plasma may be more beneficial than sipping on serum. However, it’s important to note that not all proteins are created equal: while some (like albumin) are found at high concentrations in both serum and
Why is it important to know the difference?
While it may not seem important to know the difference between serum and plasma, this knowledge is helpful in various disciplines.
How does this affect your health?
Plasma is a straw-colored liquid that makes up 55% of human blood. It contains nutrients, proteins, electrolytes, and hormones. Plasma helps carry these vital elements throughout your body and keeps you healthy.
The serum is the clear, watery plasma that remains after cells and clotting factors have been removed. The serum contains no cells or insoluble materials. It is used in medical tests because it’s easier to study than whole blood.
When it comes to your health, serum vs plasma doesn’t make much difference. Both substances are essential for keeping you alive and functioning properly.
However, if you’re ever in need of a transfusion, it’s important to know which type of blood you’re receiving; if you need a blood transfusion, make sure you get the right type! Ask your doctor or nurse if you’re not sure what type of blood you need. They’ll be happy to help. And remember, plasma is always good for you!
The benefits of choosing serum over plasma
The serum is the preferred medium for culturing cells and maintaining cell lines, while plasma is often used in coagulation studies. The proteins and other molecules present in serum provide a complex environment that supports cell growth and proliferation while also helping to maintain the stability of cellular structures.
In addition, the serum contains important growth factors that promote wound healing and tissue regeneration. Additionally, serum can be used to isolate high-quality RNA or DNA from tissues or cells, making it an essential tool for molecular biology research.
Compared to serum, plasma is less complex and contains fewer proteins and growth factors. However, plasma does contain clotting factors that can be useful in certain experiments. Ultimately, the choice of serum or plasma depends on the specific research question being asked and the desired outcome of the experiment.
Why you should consider serums for skincare, haircare, and more?
One reason you may want to consider using a serum in place of plasma involves their different texture profiles. While both are liquids, serums tend to be thicker than plasmas because they contain fewer water molecules per milliliter when compared with plasma or other fluids.
This means that your body absorbs them more quickly – which can make them better for certain purposes, such as moisturizing creams after shaving.
Plasma A big difference between these two products is what they treat on the surface versus deep within pores and skin tissues: while serum typically treats conditions on top layers of skin, plasma goes below the surface to work on problems like inflammation and acne.
- Serums are great for moisturizing the skin after shaving.
- Plasma treats conditions on top layers of skin while serum goes below the surface to work on problems like inflammation and acne.
- Some people find that serum leaves their skin feeling tacky after application, while others prefer how plasma makes their skin feel tighter and smoother.
Also read: Is Blood a Connective Tissue?
Conclusion
Blood is made up of two different components: plasma and serum. The liquid component is plasma, whereas the protein-rich component is serum.
In the body, they serve different purposes: plasma distributes nutrients and oxygen to cells, whereas serum stores antibodies that fight illness. The serum also contains clotting factors, which aid in preventing blood loss.
FAQs:
Are antibodies present in the serum?
Yes, natural antibodies are present in the serum of a healthy person. The most prominent antibody found in the serum is IgG.
Does plasma also contain antibodies?
In plasma, there is the presence of water, salt, and enzymes. Besides, there is also the presence of antibodies, clotting factors, and proteins like albumin and fibrinogen.