Cellulitis Risk Factors [Causes, and Treatment]
Overview I Symptoms I Risk factor I Diagnosis I Treatment I Complication I Prevention
What is cellulitis?
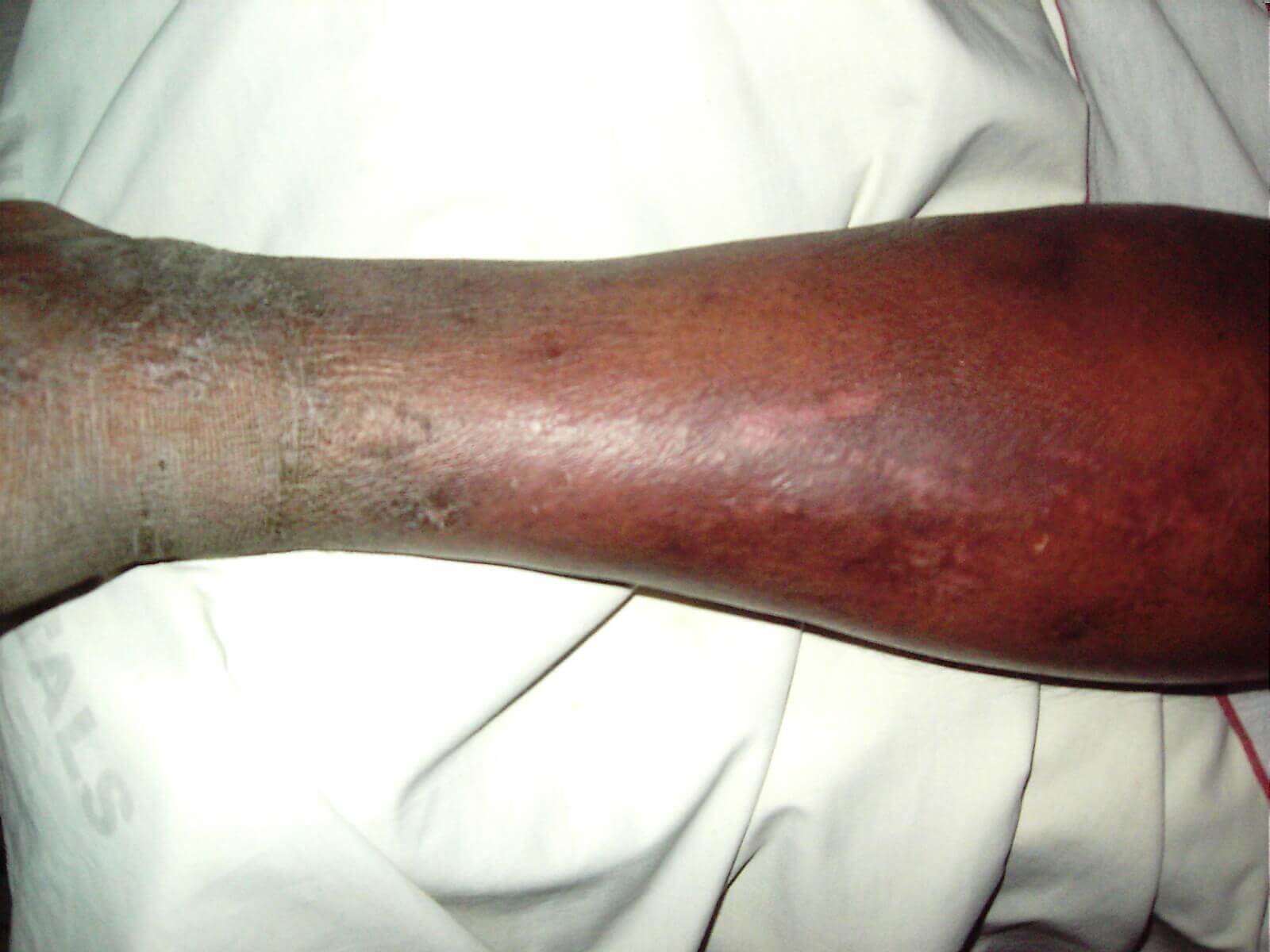
Cellulitis is defined as the common bacterial skin infection which may first appear as a red, swollen area that feels hot and tender to the touch.
The redness and swelling often spread rapidly. The border of the area of redness is generally not sharp and the skin may be swollen. While redness often turns white when pressure is applied. It is usually painful. It especially affects the dermis and subcutaneous fat.
Here you will learn about Cellulitis Risk Factors, Causes, and Treatment.
In the most case skin of the lower legs is affected, although the infection can occur anywhere on the body or face. The leg is typically affected in the following break of the skin. It can also spread to the lymph node and bloodstream. For a facial infection, a break in the skin beforehand is not usually in the case.
The bacteria most commonly used are streptococci and Staphylococcus aureus. Diagnosis of cellulitis is usually based on the presenting signs and symptoms, while cell culture is rarely possible. Before making a diagnosis, more serious, infection such as underlying bone infection or necrotizing fasciitis should be ruled out.
If cellulitis is not treated, the infection may become life-threatening. Everyone should get medical help right after developing these signs and symptoms.
Potential complication includes the formation of the abscess. Around 95% of people get better after seven to ten days of the treatment. Those with diabetes, however, often, have worse outcomes.
Pictures of cellulitis
Cellulitis symptoms
The symptoms of cellulitis may include:
- Pain and tenderness in the affected area
- Redness or inflammation of the skin
- A skin sore or rash that appears and grows quickly
- A tight, glossy, swollen appearance of skin
- A feeling of warmth in the affected area
- A central area that has an abscess with a pus formation
- A Fever
Some common symptoms of more serious cellulitis include:
- Shaking
- Chills
- Felling of illness
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Pigheadedness
- Muscle aches
- Warm skin
- Sweating
Symptoms that show cellulitis is spreading
- Drowsiness
- Lethargy
- Blistering
- Red Streaks
- You should contact your doctor immediately if any of these symptoms appear.
Cellulitis Causes and Risk factors
It occurs when certain types of bacteria enter through a cut and crack of the skin. It is commonly caused by staphylococcus aureus and streptococcus bacteria.
Skin injuries such as cut, snake bites, or surgical incisions are commonly the site of the infections. Certain factors also increase the risk of developing cellulitis.
Common risk factors include:
- A weakened immune system
- A skin condition that causes a break in the skin, such as eczema, and athlete’s foot
- Intravenous (IV) drug use
- Diabetes
- History of cellulitis
Diagnosing cellulitis
Your doctor will likely able to diagnose cellulitis on the site, but they will perform a physical examination to determine the extent of your condition. This exam might reveal:
- Swelling of the skin
- Redness and warmth of the affected area
- Swollen glands
Depending on the severity of the symptoms, your doctor may want to monitor the affected area for a few days to see if the redness and the swelling spread. in some cases, your doctor may perform blood draw or culture of the wound to test the presence of the bacteria’s.
Cellulitis Treatment
Your doctor will prescribe a 10 to a 21-day regimen of oral antibiotics to treat your infection. The length of the treatment with oral antibiotics will depend on the severity of your condition.
Even a symptom improves within a few days, it is important to take all the medication prescribed to ensure the proper treatment.
While you’re taking an antibiotic. Monitor your condition to see if symptom improve. In most cases, symptoms improve or disappear within a few days.
Your doctor may also prescribe the pain relievers.
You should rest until your symptoms improve. While you rest, raising the affected limb higher than your heart to reduce any swelling.
Contact your doctor immediately if you don’t respond to the treatment within three days after beginning a round of the antibiotics, if your symptoms get worse, or develop a fever.
It goes away within 7-10 days off of starting antibiotics. The treatment can be longer if your infection is severe. This can occur if you suffer from chronic disease if your immune system is not working properly.
People with certain preexisting medical conditions such as diabetes CLD, CKD, AKD and risk factors may need to stay in the hospital for observation during treatment. Your doctor may advise hospitalization if you may have:
- A high temperature
- A high blood pressure
- An infection that doesn’t improve with antibiotics
- A compromised immune system due to other diseases.
- You may also be hospitalized if you require IV antibiotics when oral antibiotics do not work.
Complications
Sometimes it can spread throughout the body, entering the lymph nodes and bloodstream. In rare cases, it can enter into deeper layers of the tissue. The Potential complication that can occur are:
- A blood infection
- A bone infection
- inflammation of lymph vessels
- Tissue death, or gangrene
Preventing cellulitis
If you have a break in your skin, clean it immediately and apply antibiotic ointment regularly. Cover your wound with a bandage and change it daily, until a scab is from. Watch your wound for redness, drainage, or pain. These symptoms could include infection:
- People with poor circulation or who have preexisting conditions such as diabetes, CKD, CLD, that put them at risk for cellulitis should take extra precautions, including:
- Keeping the skin moist to prevent cracking
- Treating superficial skin infections, such as athlete’s foot
- Wearing protective equipment when working or playing inspecting foot daily for a sign of infections or injury
Summary
This article is all about Cellulitis Risk Factors, Causes, and Treatment. It is spreading inflammation of subcutaneous and facial planes.
some of the causative agents of cellulitis are streptococcus Pyrogens, gram-positive organism, and other gram-negative organisms. It is presented with pain, fever, toxicity, tachycardia, and oedema.
The commonest cellulitis risk factors are diabetes and weekend immune system. The treatment of cellulitis includes rest, the elevation of part, hot fomentation, antibiotics, amnesic.
General FAQs
Is cellulitis contagious?
As you have already got an idea about the cellulitis i.e it is a skin disease. it is not contagious. it usually doesn’t spread from one person to another.
Is mrsa cellulitis contagious?
yes, MRSA ( Methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus) cellulitis is contagious. It can spread from one person to another through skin-to-skin contact.
![Cellulitis Risk Factors [Causes, and Treatment]](jpg/35692393863_be478e0830_b-150x150.jpg)
![Cellulitis Risk Factors [Causes, and Treatment]](jpg/44699140442_430d1c8d8e_b-1-150x150.jpg)
![Cellulitis Risk Factors [Causes, and Treatment]](jpg/cellulitis_of_foot_02-scaled-150x150.jpg)
![Cellulitis Risk Factors [Causes, and Treatment]](jpg/cellulitis_following_abrasion-150x150.jpg)