How to treat burn? [Principle of treatment]
Overview I Types of burn I Assement of burn I Rule of Nine I Clinical features I Principle of treatment
The burn is the thermal injury caused by dry heat. Scald is the thermal injury caused by dry heat. Most of the burn is due to heat from the hot liquids, solids, and fire. Do you know how to treat burn?
While the burn rate is similar to males and females but the underlying cause often differs. Among the women, the risk is related to the use of open cooking fire, or unsafe cookstoves, while the men risk is related to the work environment.
Alcoholism and smoking can be also considered as one of the risk factors for the burn.
Burn can also result in self-harm or the violence of the people. How to treat burn? Well, It can be easy for some people and can be the most difficult for some people.
If you know the correct way to treat it will be easier for you but if you don’t know the correct way it will be the hardest topic for you. So here, in this topic, is the principle of management for how to treat
Types of burn
There are three major categories of burns are known:
first, second, and third-degree. Each degree is dependent on the level of skin injury which is the lowest and the most severe, first degree. Including damage:
-Burns in the first grade: red, skin unblistered
-Burns in the second grade: blisters and other skin thickenings
-3rd-degree burns: broadly separated, white-like density
-Fourth-grade burns are also available. This kind of burn involves all the -symptoms and even spreads into tendons and bones throughout the flesh.
The causes of Burns are numerous, including:
Cold, boiling fluids scalding
Burns of chemical
Burns in energy
Fires, like match fire, candles, and bolts
Excessive exposure to sunshine
The burning type does not depend on the cause. Scalding, for instance, will cause all three burns, depending on the heat and duration of the skin.
Assessment of Burn
1.The extent of burn: done by Rule of 1
a.One hand+1%
b. Rule of 9
2. The depth of burn: Test sensation by a pinprick. on pinprick, if you feel pain then it is a superficial burn, and if you feel no pain, then it is a deep burn.
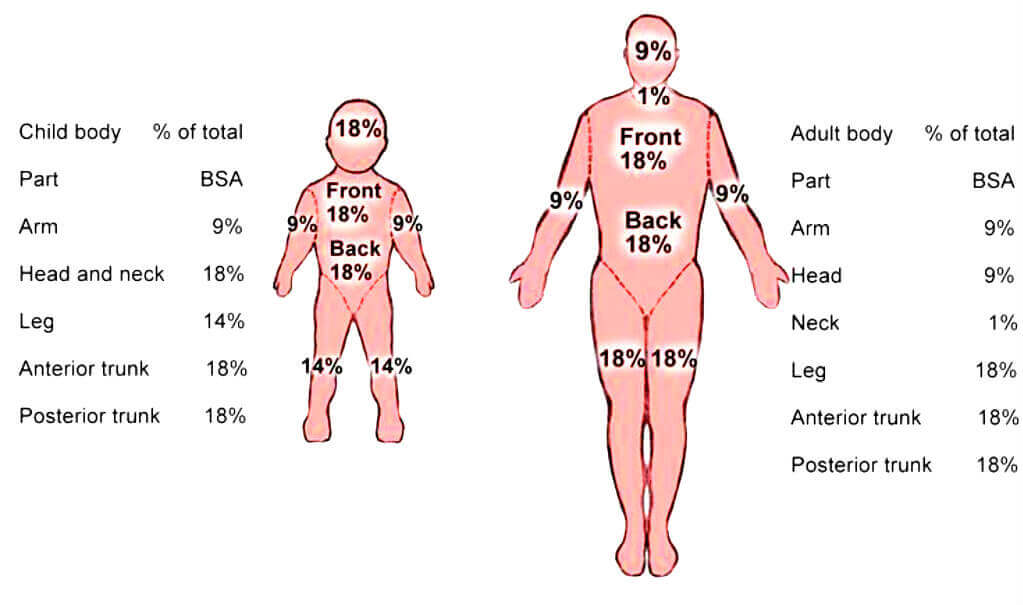
Rule of Nine
| Adults | children | Infants | |
| Head and neck | 9% | 18% | 20% |
| front of chest and abdominal wall | 9*2=18% | 18% | 10*2=20% |
| Back of chest and abdominal wall | 9*2=18% | 18% | 10*2=20% |
| Lowe limb | 18*2=36% | 13.5*2=27% | 10*2=20% |
| upper limb | 9*2=18% | 18% | 10*2=20% |
| Perineum | o.1% | 0.1% | |
| 100% | 100% | 100% |
Note: It is the head and lowers limb percentage which differs in adults and children.
Clinical features
- History of burn
- Pain
- burning
- anxious status
- Tachycardia
- Tachypnoea
- Fluid loss
- In severe degree features of shock
The tolerable temperature to human skin is 40⁰c for a brief period.
There is also a Informative article on how to treat burn in
Principle of treatment of burn
A. Prevention and treatment of burn shock by
How to treat burn? You may ask, then try out the following treatments
- Narcotic analgesic: half I/V and a half I/M
- By appropriate and adequate fluid
Appropriate fluid
Infuse plasma if it not available, give plasma substitute, if it is not available, give polyglactin (hematocele), if it not available give dextran-70, etc, if not available give electrolyte solution e.g normal saline, 5% dextrose saline, or Hartman’s solution, etc.
Adequate fluid: six ration fluids
1st 12 hours= 3 rations, 2nd 12 hours= 2 rations and 3rd 12 hours= 1 ration plus normal fluid requirement
1 ration = %of burn x weight in kg/2
=ml
B. Prevention and How to treat burn infection
- By barrier nursing
- Prophylactic antibiotics
- Prevention of tetanus
C. How to Treat burn wound
a. Open method of treatment: The patient should be isolated and keep in well ventilated dry and humidified room. Its the starting treatment for the patient.
b. Closed method of treatment: Three layers of dressing
- 1st layer: Vaseline gauze with antibiotics.
- 2nd layer: dry sterile cotton gauze.
- 3rd layer: adsorbent cotton plus cotton bandage.
- Also, consider getting a tetanus shot.
D. Prevention and treatment of burn complications.
Septic complication by blood transfusion, broad-spectrum antibiotics, and oxygen inhalation.
- Gastrointestinal hemorrhage ( curling’s ulcer) by an antacid, intravenous h₂ blocker, and blood transfusion.
- Post-burn contracture by plastic reconstruction
- Circumferential Escher by escharotomy.
These are the major fundamental of how to treat a burn. If you are treating a burn try to follow these steps. According to the
“First-degree burns typically heal on their own without treatment from a doctor. “
However, if your burn is extremely massive or if the victim is a child or old person, or if you think that your burn is a lot of severe, go to an emergency room immediately.
Conclusion
Burn or scald can be more painful. while some people with burn get fully recover with a short period of time. Above we have discussed how to treat burn. This is the principle of treatment of burn. while you may use the home remedies for burn too, but we recommend using known medical treatments instead.
This concludes our topic of How to Treat Burn.