Cases
Lump in Breast
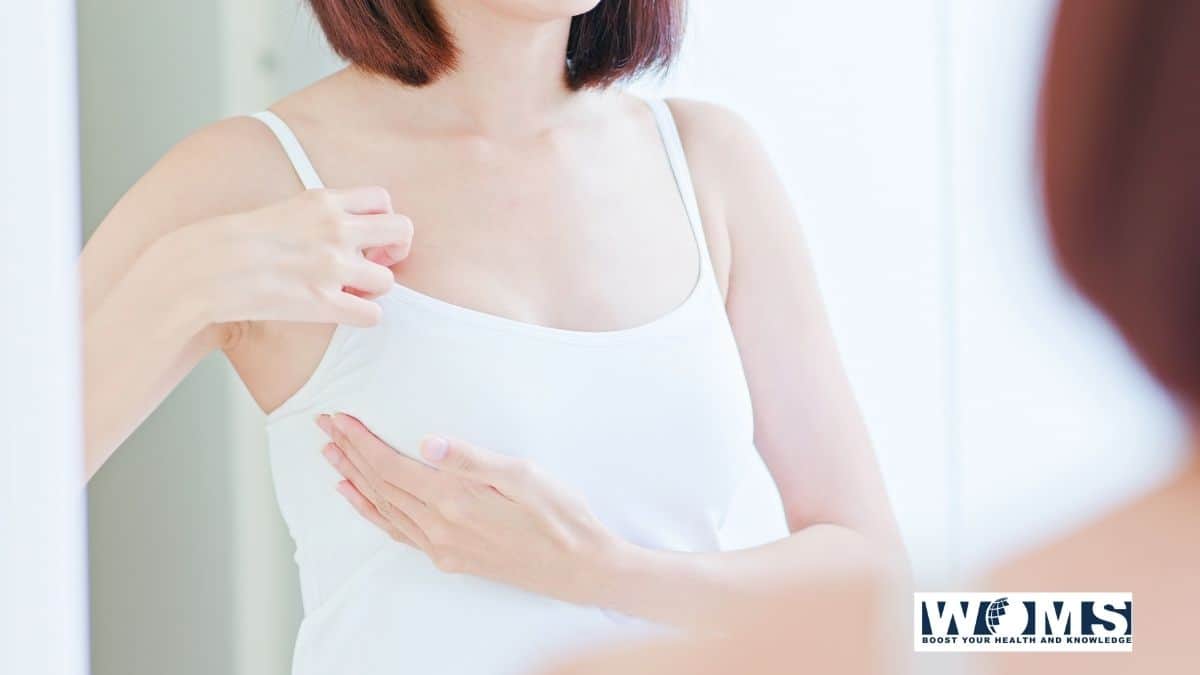

A 55-years old female complained to her family physician of a hard painless lump in the upper and outer portion o her right breast. The examination of the breast revealed the peau d’orange appearance of the skin, loss of mobility of the beast, and retraction of the nipple. The examination of axilla revealed the enlargement of axillary lymph nodes. The x-ray of the vertebral column revealed an irregular shadow in the vertebral bodies of T6 and T7 vertebrae. She was diagnosed as a case of breast cancer.
Questions
- What do you understand of a lump in the breast? What are its common causes?
- Mention the anatomical basis of the peau d’ orange appearance of the skin, retraction of the nipple, and loss of mobility of the breast.
- Name the three muscles lying deep to the base of the breast.
- What is the venous route of the spread of breast cancer?
- What is the most common site of breast cancer?
Answers:
- Any abnormal mass or thickening of the breast tissue is called lump in the breast. Lump in the breast may occur due to fibroadenoma (a benign tumor of the breast, which is usually a firm solitary mass that is mobile beneath the skin) or beast cancer (a malignant tumor of the breast, which is adherent to underlying tissue and immobile).
- The peau d’orange appearance of skin (i.e skin like an orange peel)is due to the retraction of pits of hair follicles beneath the edematous skin following the retraction of ligaments of cooper. The condition is due to the blockage of lymphatics draining the skin, leading to the stagnation of lymph and edema of skin.
Retraction of the nipple occurs due to the infiltration of lactiferous ducts by the cancer cells and their subsequent fibrosis.
- Pectoralis major, serratus anterior, and aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle of the abdomen.
- Cancer cells of the breast―posterior intercostals veins―vertebral venous plexus ―vertebral bodies
- Upper and outer quadrants of the breast.