What is an appendectomy?
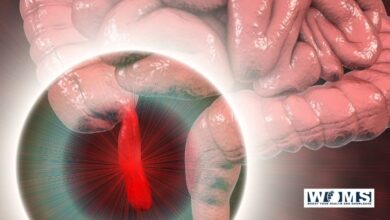
An appendectomy is the surgical removal of the vermiform appendix. It’s a conventional emergency surgery that’s performed to treat appendicitis, an inflammatory condition of the appendix.
The appendix is a worm-like diverticulum arising from the posteromedial wall of the caecum, about 2 cm below the ileocaecal orifice.
The length varies from 2 to 20 cm, with an average of 9cm. It is longer in children than in adults. The diameter is about 5mm. The lumen is quite narrow and maybe obliterated after mild-adult life.
Approaches
- Gridiron incision: The incision is placed perpendicular to the right Spinoutmbilical line at McBurney’s point (i.e., at the junction of lateral one-third and medial two-third of Spinoumbilical line). (Gridiron is a frame of cross beams to support a ship during repairs. McArthur first described this incision)
- Rutherford Morison’s muscle cutting incision (Muscles are cut upwards and laterally).
- Lanz crease incision centering at McBurney’s point-cosmetically better.
- Right lower paramedian incision/lower midline incision-when in doubt or when there is diffuse peritonitis.
- Laparoscopic approach: Becoming popular and better.
- Fowler-Weir approach: By dissecting muscle medially over the rectus.
Procedure of appendectomy
The procedure of appendectomy is detailed below.
Under general anesthesia, the skin is incised. Two layers of superficial fascia are cut. The external oblique aponeurosis is unlocked in the line of dissection. Internal oblique and transverse muscles are a rift in the range of fibers. The peritoneum is opened in the front of the dissection.
Taeniae and ileocaecal junction identify the caecum. Omentum when adherent is separated. The appendix is held with Babcock’s forceps. Mesoappendix appendicular artery is ligated. Uses of thread or silk, a purse-string suture is fixed around the base of the appendix.
The core of the appendix is creased with artery forceps and transfixed using Vicryl (absorbable). The appendix is dissected distal to the suture ligature, and the stump is cleaned with antiseptics. Purse string suture is tightened to bury the stump.
- In difficult cases,—Retrograde appendectomy can be done. In the presence of pus or burst appendix, the peritoneal cavity is drained.
- Postoperatively, IV fluids, antibiotics are given. Once bowel sounds are heard, an oral diet is started.
Complications after appendectomy
- Paralytic ileus
- Reactionary hemorrhage due to slipping of ligature of the appendicular artery
- A residual abscess (pelvic, paracolic, local, subdiaphragmatic)
- Pylephlebitis (portal pyemia)
- Adhesions, kinking, and intestinal obstruction
- Right inguinal hernia (direct)—due to injury to the ilioinguinal nerve
- Wound sepsis 10%
- Fecal fistula
- Respiratory problems and DVT
Troubles in Appendectomy
- During surgery, if the appendix is found typical, other causes for symptoms should always be looked for like Meckel’s diverticulum, Crohn’s disease, ovarian/pelvic causes in females, malignancy, etc.
- An appendicular tumor may be found. If it is in the tip, appendectomy is sufficient. It could be a carcinoid tumor. If it is in the base, right, hemicolectomy is done.
- Absence of appendix—a rare occasion can occur. Caecum and taeniae should be traced accurately before finalizing it.
- Appendicular abscess/pelvic abscess formation.
- Malignancy in the caecum is identified on the table—right hemicolectomy should be done.
- If Crohn’s disease is identified during surgery, appendicectomy can be done with care if the base of the appendix is usual. But on rare occasions, the appendix is involved by Crohn’s disease; appendectomy should not be done but treated only with antibiotics and steroids. Otherwise, fistula can develop.
Incidental appendectomy
- Here removal of the normal appendix is done at laparotomy for other conditions, e.g., hysterectomy.
- It is done in vague lower abdominal pain of doubtful severity.
- It is a useful procedure to tackle ‘Munchausen syndrome, i.e., the patient is always worried about pain abdomen and gets relieved after the procedure (psychological benefit).
Baron Hieronymus Munchausen (1797) was a German officer who fought with Russians against Turks and returned to tell tall stories. The patient presents with various stories of pain, bleeding, earlier medical or surgical therapies.
- It is done along with Ladd’s procedure for malrotation.
- It is also done during table colonic lavage (Doodleys lavage).
- It is not done in Crohn’s disease (during the acute phase), post-radiation, immunosuppression, aortoiliac grafts.