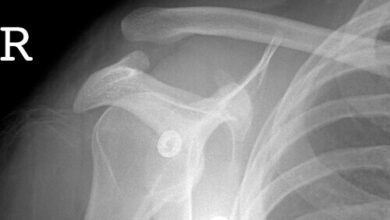
Case: Shoulder pain in an Adolescent Boy
Explanation
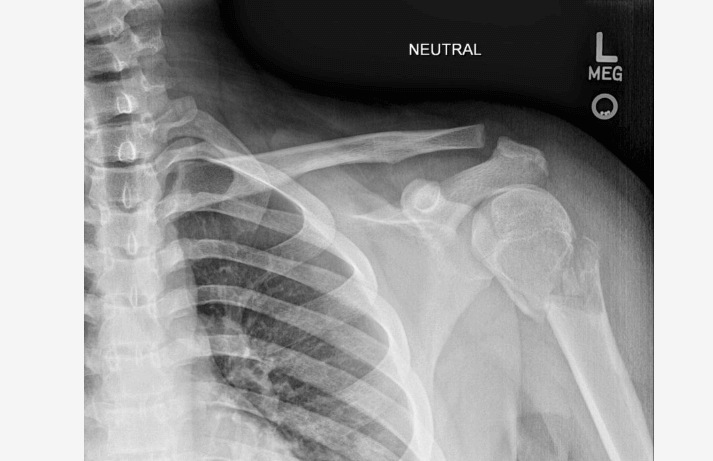
proximal humerus fractures account for <55 of fractures in children and the peak age of occurrence is 15 years old. nearly all proximal and midshaft fractures of the humerus in the pediatric population can be treated non operatively with good outcomes. bone remodeling and correction of fracture displacement are more likely to occur in younger patients before epiphyseal closure between the humeral head and the shaft occurs at age 16 to 19 years. once the epiphysis closes, remodeling is not likely to occur. currently, no widely accepted criteria exist that categorize fracture displacement according to those eligible for nonoperative treatment in children, 7 years of age, up to 60 degrees in children from 8 to 11 years of age, and up to 45 degrees in children .12 years of age.
A hanging arm cast is a common treatment modality that allows for passive fracture reduction as gravity provides traction on the humerus. the long arms hanging cast is generally continued for 3 to 4 weeks or until early healing is identified on a radiograph. in older pediatric patients with significant fracture displacement, closed reduction and percutaneous pinning may be considered as a minimally invasive option.