Bones of the hand and anatomy you must know
Bones of the hand: Carpal, Metacarpal, and Phalanges
Let’s talk about the bones of the hand, as the hand is one of the most important parts of our upper limb as well as our body. So, we must know the anatomy of the hand and the anatomy of hand bones amiably.
The hand is the end part of our upper limb. It helps in holding, moving, touching, and feeling the things around our surroundings in our daily life. The hand is made up of bones, muscles, tendons, fascia, etc. All bones of the hand provide rigidity, support, and flexibility to the hand.
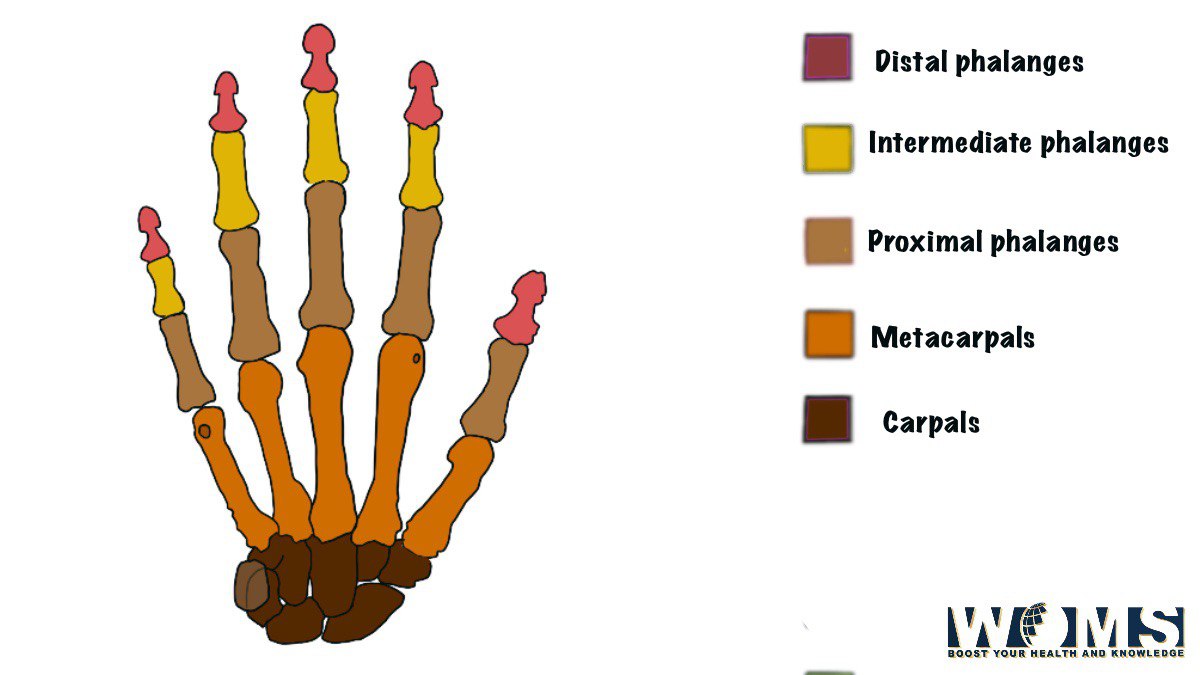
The bones of the hand are 8 carpal bones, 5 metacarpal bones, and 14 phalanges. Do you have any idea” which is the longest bone in human body? Let’s now learn about the anatomy of the hand and wrist in detail. I hope after reading this article you will get more idea about the bones of the hands.
Hand bones are also known as skeleton hands. It’s very important to know the anatomy of the hand and wrist to understand the upper extremity.
Carpal bone
Carpal bone is a set of 8 bones that are located in the wrist region of the hand and are present in irregular shapes and sizes. These 8 bones are arranged in a certain manner which is given below:
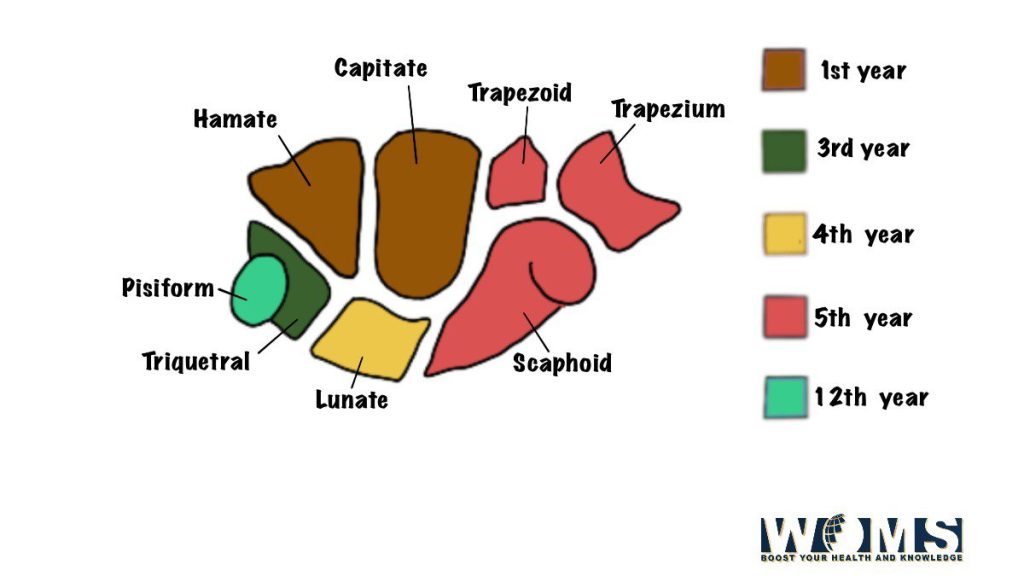
| Carpal bones arranged in a proximal row (from lateral to medial side) | Carpal bones are arranged in a distal row( from lateral to medial side) |
| 1. Scaphoid. | 1. Trapezium. |
| 2. Lunate. | 2. Trapezoid |
| 3. Triquetral | 3. Capitate. |
| 4. Pisiform | 4. Hamate. |
To remember the name of the bones of the hand present in the carpal and to make it easy for you. You can make your mnemonics or you can try this one.
Mnemonic:@ she looks too pretty try to catch her [These mnemonics help us to remember the name of carpal bone. It starts from the proximal end’s lateral side of the carpal bone to the medial end of the distal end. ]
How can we identify the carpal bones?
Carpel bones are one of the bones of hand. We can identify by following the given ways.
To identify the carpal bone we can get a clear idea from its name as it is mostly named after its shape and size.
- The scaphoid bone has a resemblance to the shape of a boat and a tubercle. It is present on the lateral side of the carpal bone.
- The name of the lunate bone is given based on its shape. The shape of the bone is like a half-moon or crescent-like.
- 3 The triquetral bone is also named based on its feature as it is present in a pyramidal shape. On the palmar surface’s distal part of the triquetral bone, there is an isolated oval facet.
- The pisiform bone has the shape of a pea. An oval facet is present on its proximal part of the dorsal surface.
- The trapezium bone is present in a quadrangular shape. It has got a crest and a groove anteriorly. It has got a sellar (concavo-convex) articular surface distally.
- The shoe of a baby is the shape presented by the trapezoid bone and in greek it means the baby’s shoe.
- the largest carpal bone is the capitate bone and among the 8 carpal bone, it has got ahead which is rounded.
- The bone has a wedge-like shape and has a hook near its base there is the presence of the hamate bone.
Detail about the carpal bones
- Scaphoid bones (scaphoid=boat-shaped): it has a prominent tubercle that projects anterolaterally from its palmar surface. it articulates with:
- the radius (proximally),
- with trapezium and trapezoid(distally)
- with the lunate bone (medially).
2. Lunate bone : (Crescentic shape): It has a large anterior -surface & narrow posterior surface. The lunate bones of the hand articulate proximally with the radius & distally with the Capitate bone.
3. Triquetralbone : (pyramidal in shape): it articulates with
- proximally with the articular disc of ulna,
- distally with the hamate bone
- anteriorly with the pisiform bone.
4. Pisiform bone (pea-shaped) – it articulates with the palmar surface of the triquetral bone. Within the tendon of flexor carpi ulnaris, it is considered a sesamoid bone
5 Trapezium : (quadrangular in shape): its palmar surface is grooved (by flexor carpi radialis tendon)&has a crest lateral to the groove. Trapezium: bones of the hands articulate proximally with scaphoid, distally with the first metacarpal bone &medially with trapezoid bone
(6)Trapezoid : (irregular in shape): it articulates with scaphoid(proximally),2nd metacarpal bone distally), trapezium (Laterally).
(7) Capitate: (bones with a head): this is the largest- carpal bone. Proximally It articulates with the scaphoid &lunate bones. distally, it articulates with the 3rd metacarpal bone.
Hamate : (bone with hook)
Hamate has got a hook anteriorly, its distal aspect is related to the deep branch of the ulnar nerve.
It articulates: proximally with triquetral, and with metacarpal bones distally i.e fourth and fifth bones of the hand, and Laterally with the Capitate bone.
What are the Articulations of 8 carpal bones?
To avoid the Bulky description about all the Bones of the hand: carpal bone, to make it easier for you to Lear articulation of all bones we easily provide you with the name of the bone with which bone all 8 carpal bones articulate.
- The scaphoid: Radius, lunate, trapezium, trapezoid, Capitate
- The lunate: Radius, scaphoid, capitate, hamate, and Triquetral.
- The triquetral: Pisiform, lunate, hamate, and articular Disc of the inferior radioulnar joint.
- The pisiform articulates only with the triquetral.
- The trapezium: Scaphoid, 1st and 2nd metacarpals and trapezoid.
- The trapezoid: Scaphoid, trapezium, 2nd metacarpal and capitate.
- The capitate: Scaphoid, lunate, hamate, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th metacarpals, and trapezoid.
- The hamate: Lunate, triquetral, capitate, and 4th and 5th metacarpals.
Which metacarpal bone is more likely to get fractured
The most common fracture of carpus bone is the fracture of the scaphoid and mainly occurs due to the fall of an individual with its outstretched hand or the top of the finger.
The Narrow Waist of the scaphoid bone is the location where the fracture occurs. Tenderness in the anatomical snuff box is seen clinically due to this fracture. In the Scaphoid bone, the Blood vessels mostly enter through both ends.
But in about 10% to 20 % of cases, all blood vessel supplies to the proximal segment of the carpal enter it Through its distal pole. Avascular necrosis occurs in a condition where the waist of the Scaphoid is fractured and the proximal segment gets deprived of Blood supply.
Metacarpal
The metacarpal is also one of the bones of the hand. 5 miniature, long bones named as 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th metacarpal from lateral to the medial side. Each one has got ahead (distally), a shaft, and a base at the proximal end.
Head: the head is round. It has got an articular surface that extends more anteroposteriorly than Laterally. It extends on the palmar surface than on the dorsal surface. It also makes knuckles during flexion.
Shaft: Palmar surface is concave while the dorsal surface has a flat triangular area which is on the distal part.
Base: There is an irregular expansion in the base which lies on the proximal end.
Detail about each metacarpal bone
1st metacarpal: It is the shortest and stoutest bones of hand which is Occupied by a concavo-convex in its base.
The articular surface for the trapezium. Its anterolateral surface is larger than the anteromedial.
2nd metacarpal: The base is grooved from before backward. The groove on the base of the medial edge is deeper than the lateral edge. An articular strip present on the medial side of the base presents a constriction in the middle.
3rd metacarpal: a styloid process is present on the base which is projecting up from the dorsolateral corner. The base of the lateral side bears an articular strip that is constricted in the middle.
4th metacarpal: Two small oval facets are present on the base on its lateral side. The third metacarpal has a single elongated facet on its medial side for the 5th metacarpal.
5th metacarpal: (Anatomy of the hand bones and base of the 5th metacarpal) an elongated articular strip is present on the base which is for the lateral side of the 4th metacarpal. the base of the medial side is non-articular and bears a tubercle.
Phalanges
THE PHALANGES are the bones of the hand. They constitute the bones of the finger each of the medial 4 Fingers has three phalanges which are proximal, medial & distal respectively while the thumb has got 2 phalanges which are proximal and distal. Each phalanx is a miniature long bone having a shaft and 2-ends.
Base (proximal end): The proximal phalanx has a base that carries an oval concave facet for articulation with the head of the metacarpal bone, while the base of the middle of the terminal phalanx Carries 2 small concave Facets separated by a smooth ridge
(b) head (Distal end): Head of the middle and proximal phalanx has a pulley, shaped articular surface while the head, the terminal phalanx is tapering nonarticular.
Takeaway
The hand is an important part of our body. It is important to know about the anatomy of hand. The bones of the hands are 8 carpal bones, 5 metacarpal bones, and 14 phalanges. Carpal bone is a set of 8 bones that are located in the wrist region of the hand and are present in irregular shapes and sizes.
The most common fracture of carpus bone is the fracture of the scaphoid and mainly occurs due to falling of an individual with its outstretched hand or the top of the finger.5 miniature, long bones named as 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th metacarpal from lateral to the medial side.
Phalanges, each one has got ahead (distally), shaft, and a base at the proximal end. They constitute the bones of the finger each of the medial 4 Fingers has three phalanges which are proximal, medial &distal respectively while the thumb has got 2 phalanges which are proximal and distal. Each phalanx is a miniature long bone having a shaft and 2-ends.
I think after reading this article you know a great amount about the anatomy of the bones of the hand.
Additional images